Oxytocin Receptor Activation Rescues Opioid-Induced Respiratory Depression by Systemic Fentanyl in the Rat
- PMID: 33990416
- PMCID: PMC8407530
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.121.000535
Oxytocin Receptor Activation Rescues Opioid-Induced Respiratory Depression by Systemic Fentanyl in the Rat
Abstract
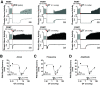
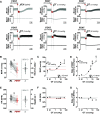
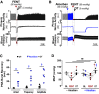
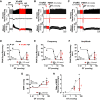
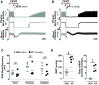
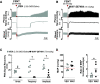
Opioid overdose intervention by naloxone, a high affinity receptor antagonist, reverses opioid-induced respiratory depression (OIRD) and analgesia by displacing opioids. Systemic naloxone stimulates release of the hypothalamic neuropeptide oxytocin, which has analgesic properties and participates in cardiorespiratory homeostasis. To test the hypothesis that oxytocin can reverse OIRD, we assessed the rescue potential of graded doses (0, 0.1, 2, 5, 10, 50 nmol/kg, i.v.) of oxytocin to counter fentanyl (60 nmol/kg, i.v.)-induced depression of neural inspiration indexed by recording phrenic nerve activity (PNA) in anesthetized (urethane/α-chloralose), vagotomized, and artificially ventilated rats. Oxytocin dose-dependently rescued fentanyl OIRD by almost immediately reversing PNA burst arrest (P = 0.0057) and restoring baseline burst frequency (P = 0.0016) and amplitude (P = 0.0025) at low but not high doses, resulting in inverted bell-shaped dose-response curves. Oxytocin receptor antagonism (40 nmol/kg, i.v.) prevented oxytocin reversal of OIRD (arrest: P = 0.0066, frequency: P = 0.0207, amplitude: P = 0.0022). Vasopressin 1A receptor (V1aR) antagonism restored high-dose oxytocin efficacy to rescue OIRD (P = 0.0170 to P < 0.0001), resulting in classic sigmoidal dose-response curves, and prevented (P = 0.0135) transient hypertension from V1aR cross-activation (P = 0.0275). Alone, vasopressin (5 nmol/kg, i.v.) failed to reverse fentanyl respiratory arrest (P = 0.6184). The nonpeptide oxytocin receptor agonist WAY-267464 (75 nmol/kg, i.v.), which has V1aR antagonist properties, quickly reversed fentanyl OIRD (P < 0.0001), with rapid recovery of PNA frequency (P = 0.0011) and amplitude (P = 0.0044) without adverse hemodynamic consequences (P = 0.9991). Findings indicate that peptide and nonpeptide agonist activation of oxytocin receptors without V1aR cross-activation rescues fentanyl OIRD. Oxytocin receptor agonists could be lifesaving resuscitation agents that enhance rather than interrupt opioid analgesia. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Oxytocin receptor activation produces analgesia. Here, we demonstrate that activation by the US Food and Drug Administration-approved agonist oxytocin and the nonpeptide partial agonist WAY-267464 can each reverse fentanyl cardiorespiratory depression. Selective targeting of oxytocin receptors for resuscitation from opioid overdose, alone or in combination with an opioid antagonist, could eliminate or attenuate negative side effects associated with traditional opioid receptor antagonism.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Altura BM, Altura BT (1984) Actions of vasopressin, oxytocin, and synthetic analogs on vascular smooth muscle. Fed Proc 43:80–86. - PubMed
-
- American Society of Addiction Medicine (2020) The ASAM National Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder: 2020 focused update. J Addict Med 14(2S, Suppl 1):1–91. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson RL, Suratt PM, Wilhoit SC, Recant L (1985) Naloxone improves sleep apnea in obese humans. Int J Obes 9:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Bicknell RJ, Zhao BG, Chapman C, Heavens RP, Sirinathsinghji DJ (1988) Opioid inhibition of secretion from oxytocin and vasopressin nerve terminals following selective depletion of neurohypophysial catecholamines. Neurosci Lett 93:281–286. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

