Molecular mechanisms of ion conduction and ion selectivity in TMEM16 lipid scramblases
- PMID: 33990555
- PMCID: PMC8121942
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22724-w
Molecular mechanisms of ion conduction and ion selectivity in TMEM16 lipid scramblases
Abstract
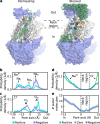
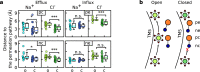
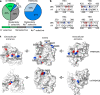
TMEM16 lipid scramblases transport lipids and also operate as ion channels with highly variable ion selectivities and various physiological functions. However, their molecular mechanisms of ion conduction and selectivity remain largely unknown. Using computational electrophysiology simulations at atomistic resolution, we identified the main ion-conductive state of TMEM16 lipid scramblases, in which an ion permeation pathway is lined by lipid headgroups that directly interact with permeating ions in a voltage polarity-dependent manner. We found that lipid headgroups modulate the ion-permeability state and regulate ion selectivity to varying degrees in different scramblase isoforms, depending on the amino-acid composition of the pores. Our work has defined the structural basis of ion conduction and selectivity in TMEM16 lipid scramblases and uncovered the mechanisms responsible for the direct effects of membrane lipids on the conduction properties of ion channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

