Impact of selenium addition to the cadmium-zinc-telluride matrix for producing high energy resolution X-and gamma-ray detectors
- PMID: 33990654
- PMCID: PMC8121847
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89795-z
Impact of selenium addition to the cadmium-zinc-telluride matrix for producing high energy resolution X-and gamma-ray detectors
Abstract
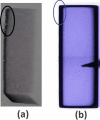
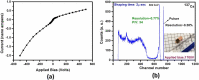
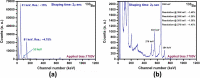
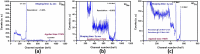
Both material quality and detector performance have been steadily improving over the past few years for the leading room temperature radiation detector material cadmium-zinc-telluride (CdZnTe). However, although tremendous progress being made, CdZnTe still suffers from high concentrations of performance-limiting defects, such as Te inclusions, networks of sub-grain boundaries and compositional inhomogeneity due to the higher segregation coefficient of Zn. Adding as low as 2% (atomic) Se into CdZnTe matrix was found to successfully mitigate many performance-limiting defects and provide improved compositional homogeneity. Here we report record-high performance of Virtual Frisch Grid (VFG) detector fabricated from as-grown Cd0.9Zn0.1Te0.98Se0.02 ingot grown by the Traveling Heater Method (THM). Benefiting from superior material quality, we achieved superb energy resolution of 0.77% at 662 keV (as-measured without charge-loss correction algorithms) registered at room temperature. The absence of residual thermal stress in the detector was revealed from white beam X-ray topographic images, which was also confirmed by Infra-Red (IR) transmission imaging under cross polarizers. Furthermore, neither sub-grain boundaries nor their networks were observed from the X-ray topographic image. However, large concentrations of extrinsic impurities were revealed in as-grown materials, suggesting a high likelihood for further reduction in the energy resolution after improved purification of the starting material.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Schlesinger TE, et al. Cadmium zinc telluride and its use as a nuclear radiation detector material. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2001;32:103. doi: 10.1016/S0927-796X(01)00027-4. - DOI
-
- Yang, G. & James, R. B. In Physics, Defects, Hetero- and Nano-structures, Crystal Growth, Surfaces and Applications Part II (ed. Triboulet, R. et al.) 214 (Elsevier, 2009).
-
- Harrison FA, et al. The nuclear spectroscopic telescope array (NuSTAR) high energy X-ray mission. Astrophys. J. 2013;770:103. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/770/2/103. - DOI
-
- Krawczynski HS, et al. X-ray polarimetry with the Polarization Spectroscopic Telescope Array (PolSTAR) Astropart. Phys. 2016;75:8. doi: 10.1016/j.astropartphys.2015.10.009. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

