Druggability of lipid metabolism modulation against renal fibrosis
- PMID: 33990764
- PMCID: PMC8888625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-021-00660-1
Druggability of lipid metabolism modulation against renal fibrosis
Abstract
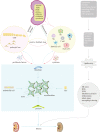
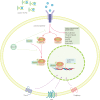
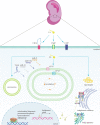
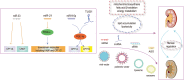
Renal fibrosis contributes to progressive damage to renal structure and function. It is a common pathological process as chronic kidney disease develops into kidney failure, irrespective of diverse etiologies, and eventually leads to death. However, there are no effective drugs for renal fibrosis treatment at present. Lipid aggregation in the kidney and consequent lipotoxicity always accompany chronic kidney disease and fibrosis. Numerous studies have revealed that restoring the defective fatty acid oxidation in the kidney cells can mitigate renal fibrosis. Thus, it is an important strategy to reverse the dysfunctional lipid metabolism in the kidney, by targeting critical regulators of lipid metabolism. In this review, we highlight the potential "druggability" of lipid metabolism to ameliorate renal fibrosis and provide current pre-clinical evidence, exemplified by some representative druggable targets and several other metabolic regulators with anti-renal fibrosis roles. Then, we introduce the preliminary progress of noncoding RNAs as promising anti-renal fibrosis drug targets from the perspective of lipid metabolism. Finally, we discuss the prospects and deficiencies of drug targeting lipid reprogramming in the kidney.
Keywords: anti-renal fibrosis; drug targets; fatty acid oxidation; lipid metabolism; noncoding RNA.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao X, Kwan JYY, Yip K, Liu PP, Liu FF. Targeting metabolic dysregulation for fibrosis therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019:1–19:57–75. - PubMed
-
- Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:309–26. - PubMed
-
- Chen DQ, Chen H, Chen L, Vaziri ND, Wang M, Li XR, et al. The link between phenotype and fatty acid metabolism in advanced chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32:1154–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

