Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the antidepressant actions of lactate
- PMID: 33990772
- PMCID: PMC8760055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01122-0
Role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the antidepressant actions of lactate
Abstract
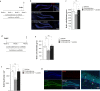
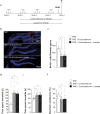
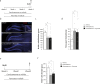
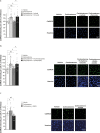
In addition to its role as a neuronal energy substrate and signaling molecule involved in synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation, recent evidence shows that lactate produces antidepressant effects in animal models. However, the mechanisms underpinning lactate's antidepressant actions remain largely unknown. In this study, we report that lactate reverses the effects of corticosterone on depressive-like behavior, as well as on the inhibition of both the survival and proliferation of new neurons in the adult hippocampus. Furthermore, the inhibition of adult hippocampal neurogenesis prevents the antidepressant-like effects of lactate. Pyruvate, the oxidized form of lactate, did not mimic the effects of lactate on adult hippocampal neurogenesis and depression-like behavior. Finally, our data suggest that conversion of lactate to pyruvate with the concomitant production of NADH is necessary for the neurogenic and antidepressant effects of lactate.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Q, Jie W, Liu J-H, Yang J-M, Gao T-M. An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview. Glia. 2017;65:1227–50. - PubMed
-
- Magistretti PJ, Allaman I. Lactate in the brain: from metabolic end-product to signalling molecule. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19:235–49. - PubMed
-
- Allen NJ. Astrocyte regulation of synaptic behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:439–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

