Enkephalin release from VIP interneurons in the hippocampal CA2/3a region mediates heterosynaptic plasticity and social memory
- PMID: 33990774
- PMCID: PMC8590711
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01124-y
Enkephalin release from VIP interneurons in the hippocampal CA2/3a region mediates heterosynaptic plasticity and social memory
Abstract
The hippocampus contains a diverse array of inhibitory interneurons that gate information flow through local cortico-hippocampal circuits to regulate memory storage. Although most studies of interneurons have focused on their role in fast synaptic inhibition mediated by GABA release, different classes of interneurons express unique sets of neuropeptides, many of which have been shown to exert powerful effects on neuronal function and memory when applied pharmacologically. However, relatively little is known about whether and how release of endogenous neuropeptides from inhibitory cells contributes to their behavioral role in regulating memory formation. Here we report that vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-expressing interneurons participate in social memory storage by enhancing information transfer from hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons to CA2 pyramidal neurons. Notably, this action depends on release of the neuropeptide enkephalin from VIP neurons, causing long-term depression of feedforward inhibition onto CA2 pyramidal cells. Moreover, VIP neuron activity in the CA2 region is increased selectively during exploration of a novel conspecific. Our findings, thus, enhance our appreciation of how GABAergic neurons can regulate synaptic plasticity and mnemonic behavior by demonstrating that such actions can be mediated by release of a specific neuropeptide, rather than through classic fast inhibitory transmission.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
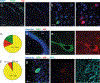
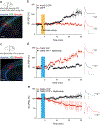
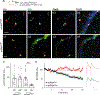
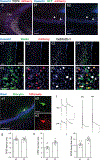
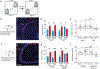
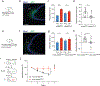
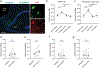
References
-
- Letzkus JJ, Wolff SBE, Meyer EMM, Tovote P, Courtin J, Herry C, et al. A disinhibitory microcircuit for associative fear learning in the auditory cortex. Nature. 2011;480:331–335. - PubMed
-
- Letzkus JJ, Wolff SBE, Lüthi A. Disinhibition, a Circuit Mechanism for Associative Learning and Memory. Neuron. 2015;88:264–276. - PubMed
-
- Krabbe S, Paradiso E, D’Aquin S, Bitterman Y, Courtin J, Xu C, et al. Adaptive disinhibitory gating by VIP interneurons permits associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1834–1843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

