The diverse effects of brain glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors on ingestive behaviour
- PMID: 33990944
- PMCID: PMC8787734
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15535
The diverse effects of brain glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors on ingestive behaviour
Abstract
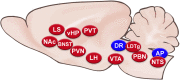
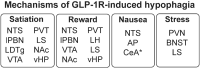
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is well known as a gut hormone and also acts as a neuropeptide, produced in a discrete population of caudal brainstem neurons that project widely throughout the brain. GLP-1 receptors are expressed in many brain areas of relevance to energy balance, and stimulation of these receptors at many of these sites potently suppresses food intake. This review surveys the current evidence for effects mediated by GLP-1 receptors on feeding behaviour at a wide array of brain sites and discusses behavioural and neurophysiological mechanisms for the effects identified thus far. Taken together, it is clear that GLP-1 receptor activity in the brain can influence feeding by diverse means, including mediation of gastrointestinal satiation and/or satiety signalling, suppression of motivation for food reward, induction of nausea and mediation of restraint stress-induced hypophagia, but many questions about the organization of this system remain. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed issue on GLP1 receptor ligands (BJP 75th Anniversary). To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v179.4/issuetoc.
Keywords: GLP-1; feeding behavior; food reward; gut-brain communication; satiation; satiety.
© 2021 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reappraising the role of the vagus nerve in GLP-1-mediated regulation of eating.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):584-599. doi: 10.1111/bph.15603. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34185884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) signalling in the brain: From neural circuits and metabolism to therapeutics.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):600-624. doi: 10.1111/bph.15682. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34519026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain GLP-1 and the regulation of food intake: GLP-1 action in the brain and its implications for GLP-1 receptor agonists in obesity treatment.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):557-570. doi: 10.1111/bph.15638. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34323288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor ligands in the gut.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):727-742. doi: 10.1111/bph.15611. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34235727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic responses and benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):526-541. doi: 10.1111/bph.15485. Epub 2021 May 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33822370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The estrogenic reduction in water intake stimulated by dehydration involves estrogen receptor alpha and a potential role for GLP-1.Physiol Behav. 2024 Mar 15;276:114484. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2024.114484. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Physiol Behav. 2024. PMID: 38331374 Free PMC article.
-
A new apparatus to analyze meal-related ingestive behaviors in rats fed a complex multi-food diet.Physiol Behav. 2022 Aug 1;252:113824. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2022.113824. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Physiol Behav. 2022. PMID: 35472328 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptors in the Gustatory Cortex Influence Food Intake.J Neurosci. 2023 Jun 7;43(23):4251-4261. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1668-22.2023. Epub 2023 May 1. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37127362 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways in obesity: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 28;7(1):298. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01149-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36031641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Semaglutide Treatment in Rats Leads to Daily Excessive Concentration-Dependent Sucrose Intake.J Endocr Soc. 2023 Jun 7;7(7):bvad074. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvad074. eCollection 2023 Jun 5. J Endocr Soc. 2023. PMID: 37388574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Christopoulos, A. , Davenport, A. P. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Sharman, J. L. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , & CGTP Collaborators . (2019). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2019/20: G protein‐coupled receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176(Suppl 1), S21–S141. 10.1111/bph.14748 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Fabbro, D. , Kelly, E. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Sharman, J. L. , Southan, C. , Davies, J. A. , & CGTP Collaborators . (2019). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2019/20: Enzymes. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176, S297–S396. 10.1111/bph.14752 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Mathie, A. , Peters, J. A. , Veale, E. L. , Striessnig, J. , Kelly, E. , Armstrong, J. F. , Faccenda, E. , Harding, S. D. , Pawson, A. J. , Sharman, J. L. , & CGTP Collaborators . (2019). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2019/20: Ion channels. British Journal of Pharmacology, 176, S142–S228. 10.1111/bph.14749 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alhadeff, A. L. , Baird, J.‐P. , Swick, J. C. , Hayes, M. R. , & Grill, H. J. (2014). Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor signaling in the lateral parabrachial nucleus contributes to the control of food intake and motivation to feed. Neuropsychopharmacology: Official Publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 39(9), 2233–2243. 10.1038/npp.2014.74 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alhadeff, A. L. , & Grill, H. J. (2014). Hindbrain nucleus tractus solitarius glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor signaling reduces appetitive and motivational aspects of feeding. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 307(4), R465–R470. 10.1152/ajpregu.00179.2014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

