The role of disinfectants and sanitizers during COVID-19 pandemic: advantages and deleterious effects on humans and the environment
- PMID: 33991301
- PMCID: PMC8122186
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14429-w
The role of disinfectants and sanitizers during COVID-19 pandemic: advantages and deleterious effects on humans and the environment
Abstract
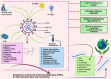
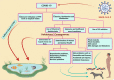
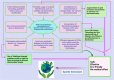
Disinfectants and sanitizers are essential preventive agents against the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic; however, the pandemic crisis was marred by undue hype, which led to the indiscriminate use of disinfectants and sanitizers. Despite demonstrating a beneficial role in the control and prevention of COVID-19, there are crucial concerns regarding the large-scale use of disinfectants and sanitizers, including the side effects on human and animal health along with harmful impacts exerted on the environment and ecological balance. This article discusses the roles of disinfectants and sanitizers in the control and prevention of the current pandemic and highlights updated disinfection techniques against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This article provides evidence of the deleterious effects of disinfectants and sanitizers exerted on humans, animals, and the environment as well as suggests mitigation strategies to reduce these effects. Additionally, potential technologies and approaches for the reduction of these effects and the development of safe, affordable, and effective disinfectants are discussed, particularly, eco-friendly technologies using nanotechnology and nanomedicine.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disinfectants; Environment; Hazard; Prevention; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic overview of metal nanoparticles as alternative disinfectants for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Feb 19;206(3):111. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03818-z. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38372809 Review.
-
A comprehensive health effects assessment of the use of sanitizers and disinfectants during COVID-19 pandemic: a global survey.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jun;30(28):72368-72388. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-27197-6. Epub 2023 May 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37166731 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Practices Regarding Safe Household Cleaning and Disinfection for COVID-19 Prevention - United States, May 2020.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Jun 12;69(23):705-709. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6923e2. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020. PMID: 32525852 Free PMC article.
-
[Disinfectants during the COVID-19 pandemic: a challenge].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022 Jan;65(1):86-95. doi: 10.1007/s00103-021-03457-z. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022. PMID: 34878564 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Environmental and health impacts of spraying COVID-19 disinfectants with associated challenges.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Dec;29(57):85648-85657. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16575-7. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 34599438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Determination of volatile impurities and ethanol content in ethanol-based hand sanitizers: Compliance and toxicity.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Aug 8;13:101709. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101709. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39247052 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical Incompatibility of Lubricating Gel Formulation Reduces Antibacterial Activity of Chlorhexidine Gluconate: In Vitro Study in Northern Thailand.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 27;19(19):12285. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912285. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231587 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance in the COVID-19 Landscape: Is There an Opportunity for Anti-Infective Antibodies and Antimicrobial Peptides?Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 2;13:921483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.921483. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tackling transmission of infectious diseases: A probiotic-based system as a remedy for the spread of pathogenic and resistant microbes.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Jul;17(7):e14529. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14529. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39045894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Missense mutations in spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant contribute to the alteration in viral structure and interaction with hACE2 receptor.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022 Sep;10(9):e683. doi: 10.1002/iid3.683. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022. PMID: 36039645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn J, Eum K, Kim Y, Oh SW, Kim YJ, Lee M. Assessment of the dermal and ocular irritation potential of alcohol hand sanitizers containing aloe vera with in vitro and in vivo methods. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2010;6:397–404. doi: 10.1007/s13273-010-0053-y. - DOI
-
- Al-Gheethi A, Al-Sahari M, Malek MA, Noman E, Al-Maqtari Q, Mohamed R, Talip BA, Alkhadher S, Hossain MS. Disinfection methods and survival of SARS-CoV-2 in the environment and contaminated materials: a bibliometric analysis. Sustainability. 2020;12(18):7378. doi: 10.3390/su12187378. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

