A novel nano therapeutic using convalescent plasma derived exosomal (CPExo) for COVID-19: A combined hyperactive immune modulation and diagnostics
- PMID: 33991505
- PMCID: PMC8116126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109497
A novel nano therapeutic using convalescent plasma derived exosomal (CPExo) for COVID-19: A combined hyperactive immune modulation and diagnostics
Abstract
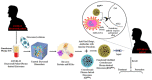
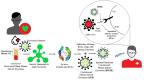
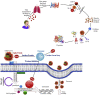
Extracellular vesicles like exosomes are important therapeutic tactics for treating COVID -19. By utilizing convalescent plasma derived exosomes (CPExo) from COVID-19 recovered persistence could accelerate the treatment strategies in the current state of affairs. Adequate literature has shown that administering the exosome to the in vivo system could be beneficial and could target the pathogens in an effective and precise manner. In this hypothesis we highlight the CPExo instead of convalescent plasma (CP), perhaps to dispense of exosomes are gratified and it's more effectively acquired immune response conferral through antibodies. COVID-19 convalescent plasma has billions of exosomes and it has aptitudes to carry molecular constituents like proteins, lipids, RNA and DNA, etc. Moreover, exosomes are capable of recognizing antigens with adequate sensitivity and specificity. Many of these derivatives could trigger an immune modulation into the cells and act as an epigenetic inheritor response to target pathogens through RNAs. COIVID-19 resistance activated plasma-derived exosomes are either responsible for the effects of plasma beyond the contained immune antibodies or could be inhibitory. The proposed hypothesis suggests that preselecting the plasma-derived antibodies and RNAs merged exosomes would be an optimized therapeutic tactic for COVID-19 patients. We suggest that, the CPExo has a multi-potential effect for treatment efficacy by acting as immunotherapeutic, drug carrier, and diagnostic target with noncoding genetic materials as a biomarker.
Keywords: COVID-19; Convalescent plasma; Diagnosis; Drug delivery; Exosomes; Immunotherapy; miRNAs.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
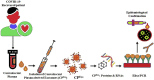
Similar articles
-
Preclinical Studies on Convalescent Human Immune Plasma-Derived Exosome: Omics and Antiviral Properties to SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:824378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824378. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35401544 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) and convalescent plasma must consider exosome involvement: Do the exosomes in convalescent plasma antagonize the weak immune antibodies?J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Oct;10(1):e12004. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12004. Epub 2020 Nov 14. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33304473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconvalescent plasma/camostat mesylate in early SARS-CoV-2 Q-PCR positive high-risk individuals (RES-Q-HR): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2021 May 17;22(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05181-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34001215 Free PMC article.
-
Convalescent blood plasma (CBP) donated by recovered COVID-19 patients - A comment.Transfus Apher Sci. 2021 Jun;60(3):103108. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2021.103108. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Transfus Apher Sci. 2021. PMID: 33678561 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Convalescent Plasma Therapy for COVID-19: Lessons from SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and H1N1 Infection.Acta Med Indones. 2021 Jan;53(1):86-95. Acta Med Indones. 2021. PMID: 33818411 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends in Drug Delivery Systems for Natural Bioactive Molecules to Treat Health Disorders: The Importance of Nano-Liposomes.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 15;14(12):2808. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122808. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional role of exosomes in viral diseases: From transmission to diagnosis and therapy.Cell Signal. 2022 Jun;94:110325. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110325. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 35367363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Studies on Convalescent Human Immune Plasma-Derived Exosome: Omics and Antiviral Properties to SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:824378. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824378. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35401544 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma-derived exosomal miRNA as potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of vector-borne diseases: A review.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 13;14:1097173. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1097173. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37125151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meet changes with constancy: Defence, antagonism, recovery, and immunity roles of extracellular vesicles in confronting SARS-CoV-2.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Dec;11(12):e12288. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12288. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 36450704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization W.H. World Heal. Organ. Geneva; Switzerland: 2020. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard.https//Covid19.Who.Int/ Accessed. 5.
-
- Davis I.D. An overview of cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000;78:179–195. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

