ROS-induced cell cycle arrest as a mechanism of resistance in polyaneuploid cancer cells (PACCs)
- PMID: 33991583
- PMCID: PMC8511226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2021.05.002
ROS-induced cell cycle arrest as a mechanism of resistance in polyaneuploid cancer cells (PACCs)
Abstract
Cancer is responsible for the deaths of millions of people worldwide each year. Once metastasized, the disease is incurable and shows resistance to all anti-cancer therapies. The already-elevated level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancer cells is further increased by therapies. The oxidative stress activates the DNA damage response (DDR) and the stressed cancer cell moves towards cell cycle arrest. Once arrested, the majority of cancer cells will undergo programmed cell death in the form of apoptosis. If the cancer cell is able to exit the cell cycle prior to cell division and enter a protected G0 state, it is able to withstand and survive therapy as a polyaneuploid cancer cell (PACC) and eventually seed resistant tumor growth.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Polyaneuploid cancer cell (PACC); Polyploid giant cancer cell (PGCC); Reactive oxygen species; Therapy resistance.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest K.J. Pienta is a consultant for CUE Biopharma, Inc., is a founder and holds equity interest in Keystone Biopharma, Inc., and receives research support from Progenics, Inc. The other authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
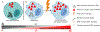
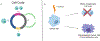

References
-
- Ferlay JA-O, et al. , Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. (1097–0215 (Electronic)). - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2020. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2020. 70(1): p. 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Norouzi S, et al. , Crosstalk in cancer resistance and metastasis. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology, 2018. 132: p. 145–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

