The mediating effect of parenting stress and couple relationship quality on the association between material hardship trajectories and maternal mental health status
- PMID: 33991944
- PMCID: PMC8217282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.04.058
The mediating effect of parenting stress and couple relationship quality on the association between material hardship trajectories and maternal mental health status
Abstract
Background: Household material hardships could have a negative impact on maternal mental health. Understanding mechanisms by which material hardship trajectories affect maternal depression and anxiety could aid health care professionals and researchers to design better interventions to improve mental health outcomes among mothers.
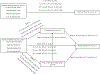
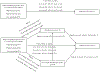
Methods: The study identified family-level mechanisms by which material hardship trajectories affect maternal depression and anxiety using Fragile Families and Child Wellbeing Study data (n = 1,645). Latent growth mixture modelling was used to identify latent classes of material hardship trajectories at Years-1, -3, and -5. Parenting stress and couple relationship quality was measured at Year-9. The outcome measures included maternal depression and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) at Year-15 based on the Composite International Diagnostic Interview - Short Form.
Results: Parenting stress mediated the association between low-increasing hardship (b = 0.020, 95% confidence interval (CI):0.003, 0.043) and maternal depression. Parenting stress also mediated the association between high-increasing hardship (b = 0.043, 95% CI:0.004, 0.092), high decreasing hardship (b = 0.034, 95% CI=0.001, 0.072), and low-increasing (b = 0.034, 95% CI:0.007, 0.066) and maternal GAD. In all models, current material hardship was directly related to maternal depression (b = 0.188, 95% CI:0.134, 0.242) and GAD (b = 0.174, 95% CI:0.091, 0.239).
Limitations: Study results need to be interpreted with caution as the FFCWS oversampled non-marital births as part of the original study design.
Conclusions: While current material hardship appears to be more related to maternal mental health, prior material hardship experiences contribute to greater parenting stress which places mothers at risk for experiencing depression and GAD later on.
Keywords: Couple relationships quality; Depression; Fragile families and child wellbeing study; Generalized anxiety disorder; Parenting stress.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abidin R, 1995. Manual for the parenting stress index, 3rd ed. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa, FL.
-
- Berryhill MB, Soloski KL, Durtschi JA, Adams RR, 2016. Family process: Early child emotionality, parenting stress, and couple relationship quality. Pers Relatsh 23, 23–41. 10.1111/pere.12109 - DOI
-
- Beverly SG, 2001. Measures of material hardship. J Poverty 5, 23–41. 10.1300/J134v05n01_02 - DOI
-
- Blane D, 2006. The life course, the social gradient, and health, In: Marmot M, Wilkinson R. (Eds.), Social Determinants of Health, 2nd ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 54–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

