Prior ischemic strokes are non-inferior for predicting future ischemic strokes than CHA2DS2-VASc score in hemodialysis patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 33992086
- PMCID: PMC8126112
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-021-02384-0
Prior ischemic strokes are non-inferior for predicting future ischemic strokes than CHA2DS2-VASc score in hemodialysis patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Background: We tested whether CHA2DS2-VASc and/or HAS-BLED scores better predict ischemic stroke and major bleeding, respectively, than their individual components in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Methods: A retrospective cohort study of a clinical database containing the medical records of 268 MHD patients with non-valvular AF (167 women, mean age 73.4 ± 10.2 years). During the median follow-up of 21.0 (interquartile range, 5.0-44.0) months, 46 (17.2%) ischemic strokes and 24 (9.0%) major bleeding events were reported.
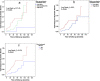
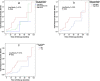
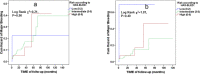
Results: Although CHA2DS2-VASc predicted ischemic stroke risk in the study population (adjusted HR 1.74 with 95% CI 1.23-2.46 for each unit of increase in CHA2DS2-VASc score, and HR of 5.57 with 95% CI 1.88-16.49 for CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥ 6), prior ischemic strokes/transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) were non-inferior in both univariate and multivariate analyses (adjusted HR 8.65 with 95% CI 2.82-26.49). The ROC AUC was larger for the prior ischemic stroke/TIA than for CHA2DS2-VASc. Furthermore, the CHA2DS2-VASc score did not predict future ischemic stroke risks in study participants who did not previously experience ischemic strokes/TIAs (adjusted HR 1.41, 95% CI: 0.84-2.36). The HAS-BLED score and its components did not have predictive abilities in discriminating bleeding risk in the study population.
Conclusions: Previous ischemic strokes are non-inferior for predicting of future ischemic strokes than the complete CHA2DS2-VASc score in MHD patients. CHA2DS2VASc scores are less predictive in MHD patients without histories of CVA/TIA. HAS-BLED scores do not predict major bleeding in MHD patients. These findings should redesign approaches to ischemic stroke risk stratification in MHD patients if future large-scale epidemiological studies confirm them.
Keywords: Bleeding; CHA2DS2-VASc; HAS-BLED; Hemodialysis; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Baber U, Howard VJ, Halperin JL, Soliman EZ, Zhang X, McClellan W, Warnock DG, Muntner P. Association of chronic kidney disease with atrial fibrillation among adults in the United States: REasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke (REGARDS) study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011;4(1):26–32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.110.957100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buiten MS, de Bie MK, Rotmans JI, Gabreëls BA, van Dorp W, Wolterbeek R, Trines SA, Schalij MJ, Jukema JW, Rabelink TJ, van Erven L. The dialysis procedure as a trigger for atrial fibrillation: new insights in the development of atrial fibrillation in dialysis patients. Heart. 2014;100(9):685–690. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-305417. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

