Knowledge, attitude and practice of physical activity promotion among physiotherapists in India during COVID 19
- PMID: 33992283
- PMCID: PMC9760009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2020.12.042
Knowledge, attitude and practice of physical activity promotion among physiotherapists in India during COVID 19
Abstract
Introduction: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic and the nationwide lockdown has increased sedentary time and physical inactivity. Physiotherapists are one of the essential health professionals who are actively involved in promoting physical activities. The study objectives included assessing knowledge of physical activity guidelines, physiotherapist attitude towards involvement in physical activities and practice of routine physical activity assessment, and its promotion among physiotherapists in India during COVID-19.
Method: In this cross-sectional survey study, the study tool was prepared using Google Forms. It consisted of sixteen questions on knowledge, attitude, and practice of physical activities among physiotherapists. Study participants were physiotherapists with a minimum of a bachelor's degree qualification and practicing in India.
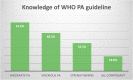
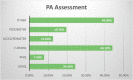
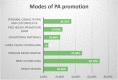
Results: One hundred and eighty responses were received from sixteen states of India. The average age of respondents was 28 years, and the average work experience of five years. This study found that only 19% of physiotherapists could give the correct answer in all three domains of WHO PA guidelines. 70% of physiotherapists found with an appropriate attitude as they met the 150 min of moderate PA per week. 68% reported that they promote physical activities in routine practice.
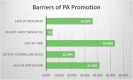
Conclusion: This study suggested the majority of physiotherapists perform physical activity assessment and promotion in routine practice in India. Most of them have an appropriate attitude towards physical activity, but very few physiotherapists have adequate knowledge of WHO physical activity guidelines. Physiotherapists should actively promote physical activities in routine practice to reduce the impairment due to physical inactivity especially during the Corona virus disease pandemic in India. Efforts should be made to increase the physical activity awareness in terms of knowledge of WHO physical activity guidelines, different assessment, and promotion strategies.
Keywords: Health professionals; Health promotion; Pandemic; Physical activity guidelines; Physical inactivity.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barrett E.M., Darker C.D., Hussey J. Promotion of physical activity in primary care: knowledge and practice of general practitioners and physiotherapists. J. Publ. Health. 2013;21:63–69. doi: 10.1007/s10389-012-0512-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous