A Probable Covid-19 Case Presented with Acute Upper Limb İschemia
- PMID: 33992721
- PMCID: PMC8118708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2021.05.003
A Probable Covid-19 Case Presented with Acute Upper Limb İschemia
Abstract
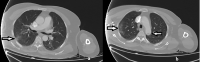
The arterial revascularization procedure is still a challenging issue in Covid-19 associated limb ischemia. Herein we aimed to present a case of a 64 year-old woman with acute ischemic signs in upper extremity who was diagnosed as a probable Covid-19 case incidentally after admission. Although late admission and failed recurrent embolectomies lead to an eventful course, intra-arterial thrombolysis seemed to present a benefitable treatment option for our patient.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

