The biosynthesis of phospholipids is linked to the cell cycle in a model eukaryote
- PMID: 33992808
- PMCID: PMC8202326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158965
The biosynthesis of phospholipids is linked to the cell cycle in a model eukaryote
Abstract
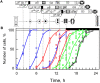
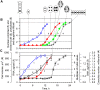
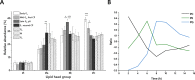
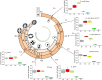
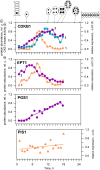
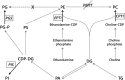
The structural challenges faced by eukaryotic cells through the cell cycle are key for understanding cell viability and proliferation. We tested the hypothesis that the biosynthesis of structural lipids is linked to the cell cycle. If true, this would suggest that the cell's structure is important for progress through and perhaps even control of the cell cycle. Lipidomics (31P NMR and MS), proteomics (Western immunoblotting) and transcriptomics (RT-qPCR) techniques were used to profile the lipid fraction and characterise aspects of its metabolism at seven stages of the cell cycle of the model eukaryote, Desmodesmus quadricauda. We found considerable, transient increases in the abundance of phosphatidylethanolamine during the G1 phase (+35%, ethanolamine phosphate cytidylyltransferase increased 2·5×) and phosphatidylglycerol (+100%, phosphatidylglycerol synthase increased 22×) over the G1/pre-replication phase boundary. The relative abundance of phosphatidylcholine fell by ~35% during the G1. N-Methyl transferases for the conversion of phosphatidylethanolamine into phosphatidylcholine were not found in the de novo transcriptome profile, though a choline phosphate transferase was found, suggesting that the Kennedy pathway is the principal route for the synthesis of PC. The fatty acid profiles of the four most abundant lipids suggested that these lipids were not generally converted between one another. This study shows for the first time that there are considerable changes in the biosynthesis of the three most abundant phospholipid classes in the normal cell cycle of D. quadricauda, by margins large enough to elicit changes to the physical properties of membranes.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Cell division; Cell structure; Desmodesmus quadricauda; Green algae; Lipid composition; Lipid metabolism.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promiscuous phospholipid biosynthesis enzymes in the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Jul;1866(7):158926. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158926. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33766680
-
Phospholipids are synthesized in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(3):597-605. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.10.011. Epub 2006 Oct 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17113814
-
Schistosoma mansoni: synthesis and release of phospholipids, lysophospholipids, and neutral lipids by schistosomula.Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jul;69(1):65-77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90172-0. Exp Parasitol. 1989. PMID: 2731586
-
Phospholipid biosynthesis in mammalian cells.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):113-28. doi: 10.1139/o03-073. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15052332 Review.
-
The Kennedy pathway--De novo synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine.IUBMB Life. 2010 Jun;62(6):414-28. doi: 10.1002/iub.337. IUBMB Life. 2010. PMID: 20503434 Review.
Cited by
-
Short Linear Motifs Orchestrate Functioning of Human Proteins during Embryonic Development, Redox Regulation, and Cancer.Metabolites. 2022 May 21;12(5):464. doi: 10.3390/metabo12050464. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35629968 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol and lipid metabolism in bees.Metabolomics. 2023 Aug 29;19(9):78. doi: 10.1007/s11306-023-02039-1. Metabolomics. 2023. PMID: 37644282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid packing and local geometry influence septin curvature sensing.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 16:2025.02.12.637894. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.12.637894. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39990479 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Systemic analysis of lipid metabolism from individuals to multi-organism systems.Mol Omics. 2024 Oct 28;20(9):570-583. doi: 10.1039/d4mo00083h. Mol Omics. 2024. PMID: 39246063 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal oscillation of phospholipids promotes metabolic efficiency.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Apr 14. doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-01885-5. Online ahead of print. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40229581
References
-
- Hartwell L.H. Nobel lecture: yeast and cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2002;22:373–394. - PubMed
-
- Hunt T. Nobel lecture: protein synthesis, proteolysis, and cell cycle transitions. Biosci. Rep. 2002;22:465–486. - PubMed
-
- Nurse P. Cyclin dependent kinases and cell cycle control (nobel lecture) ChemBioChem. 2002;3:596–603. - PubMed
-
- Renaudin J.-P., Doonan J.H., Freeman D., Hashimoto J., Hirt H., Inzé D., Jacobs T., Kouchi H., Rouzé P., Sauter M., Savouré A., Sorrell D.A., Sundaresan V., Murray J.A.H. Plant cyclins: a unified nomenclature for plant A-, B- and D-type cyclins based on sequence organization. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996;32:1003–1018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

