Replication initiation: Implications in genome integrity
- PMID: 33992866
- PMCID: PMC8296962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103131
Replication initiation: Implications in genome integrity
Abstract
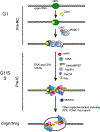
In every cell cycle, billions of nucleotides need to be duplicated within hours, with extraordinary precision and accuracy. The molecular mechanism by which cells regulate the replication event is very complicated, and the entire process begins way before the onset of S phase. During the G1 phase of the cell cycle, cells prepare by assembling essential replication factors to establish the pre-replicative complex at origins, sites that dictate where replication would initiate during S phase. During S phase, the replication process is tightly coupled with the DNA repair system to ensure the fidelity of replication. Defects in replication and any error must be recognized by DNA damage response and checkpoint signaling pathways in order to halt the cell cycle before cells are allowed to divide. The coordination of these processes throughout the cell cycle is therefore critical to achieve genomic integrity and prevent diseases. In this review, we focus on the current understanding of how the replication initiation events are regulated to achieve genome stability.
Keywords: DNA replication; Genome stability; Origin Firing; Origin Recognition Complex; Origin licensing; Pre-replication complex.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bell SP, Dutta A, DNA Replication in Eukaryotic Cells, Annual Review of Biochemistry, 71 (2002) 333–374. - PubMed
-
- Bell SP, The origin recognition complex: from simple origins to complex functions, Genes Dev, 16 (2002) 659–672. - PubMed
-
- Bleichert F, Mechanisms of replication origin licensing: a structural perspective, Current opinion in structural biology, 59 (2019) 195–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources