Evaluation of the inter and intraobserver reproducibility of the GRASP method: a goniometric method to measure the isolated glenohumeral range of motion in the shoulder joint
- PMID: 33993351
- PMCID: PMC8124032
- DOI: 10.1186/s40634-021-00352-z
Evaluation of the inter and intraobserver reproducibility of the GRASP method: a goniometric method to measure the isolated glenohumeral range of motion in the shoulder joint
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the intra and interobserver reproducibility of a new goniometric method for evaluating the isolated passive range of motion of the glenohumeral joint in an outpatient setting.
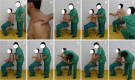
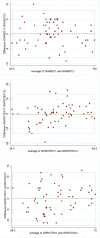
Methods: This is a prospective observational study on healthy subjects. The Glenohumeral ROM Assessment with Scapular Pinch (GRASP) method is a new method for assessing the isolated range of motion (ROM) of the glenohumeral joint (GH) by a single examiner with a clinical goniometer. It measures the isolated glenohumeral passive abduction (GH-AB), passive external rotation (GH-ER) and internal rotation (GH-IR) with the arm at 45º of abduction. These three GH ROM parameters were measured in both shoulders of 30 healthy volunteers (15 males/15 females, mean age:41.6[SD = 10.3] years). The full shoulder passive abduction, passive external rotation and internal rotation 45º of abduction were measured by the same examiners with a goniometer for comparison. One examiner made two evaluations and a second examiner made a third one. The primary outcome was the intra- and interobserver reproducibility of the measurements assessed with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and the Bland-Altman plot.
Results: The intra-observer ICC for isolated glenohumeral ROM were: 0.84 ± 0.07 for GH-ABD, 0.63 ± 0.09 for GH-ER, and 0.61 ± 0.14 for GH-IR. The inter-observer ICC for isolated glenohumeral ROM were: 0.86 ± 0.06 for GH-ABD, 0.68 ± 0.12 for GH-ER, and 0.62 ± 0.14 for GH-IR. These results were similar to those obtained for full shoulder ROM assessment with a goniometer.
Conclusion: The GRASP method is reproducible for quick assessment of isolated glenohumeral ROM.
Level of evidence: III.
Keywords: Glenohumeral joint; Goniometric; Range of motion; Shoulder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Beitzel K, Mazzocca AD, Bak K, Itoi E, Kibler WB, Mirzayan R, Imhoff AB, Calvo E, Arce G, Shea K. ISAKOS upper extremity committee consensus statement on the need for diversification of the Rockwood classification for acromioclavicular joint injuries. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2013.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

