Five-year follow-up of nivolumab treatment in Japanese patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ATTRACTION-1/ONO-4538-07)
- PMID: 33993388
- PMCID: PMC8387268
- DOI: 10.1007/s10388-021-00850-0
Five-year follow-up of nivolumab treatment in Japanese patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ATTRACTION-1/ONO-4538-07)
Abstract
Background: In the phase II ATTRACTION-1 study, nivolumab demonstrated a promising antitumor activity among Japanese patients with treatment-refractory advanced esophageal cancer. Here, we report the follow-up results of ATTRACTION-1 of > 5 years.
Methods: We enrolled patients with esophageal cancer that was refractory or intolerant to a standard chemotherapy. Then, nivolumab (3 mg/kg) was administered every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was a centrally assessed objective response rate.
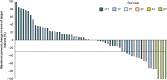
Results: Nivolumab was administered to 65 patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC). The centrally assessed objective response rate was 17.2%. The overall survival rates at 3 and 5 years were 10.9% and 6.3%, respectively. Three-year survivors tended to have more reduced target lesions. A total of 63.1% of the patients exhibited treatment-related adverse events, and no new safety signal was observed. Patients with select adverse events tended to have better overall survival than those without. No apparent chronological order was observed between the first response and the onset of select adverse events.
Conclusion: Our follow-up analysis of more than 5 years is currently the longest and is the first to demonstrate that nivolumab has long-term efficacy and safety for advanced ESCC.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Nivolumab.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Taroh Satoh received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and grants from Ono, Chugai, Yakult Honsha, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Gilead Sciences, Parexel, Daiichi Sankyo, and Astellas; honoraria from Ono, Chugai, Yakult Honsha, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Daiichi Sankyo; and travel fee from Ono outside the submitted work. Ken Kato received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and grants from Ono, MSD, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Chugai, BeiGene, and Shionogi; honoraria from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. Takashi Ura, Yasuo Hamamoto, Hirofumi Yasui, and Yuichiro Doki received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study. Takashi Kojima received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and research funding from MSD, Astellas Amgen BioPharma, Taiho, Chugai, and Shionogi; and honoraria from Ono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Astellas, Merck, and Oncolys BioPharma outside the submitted work. Takahiro Tsushima received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and honorarium from Ono outside the submitted work. Shuichi Hironaka received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ono, Taiho, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Chugai, Nippon kayaku, Tsumura, Sanofi, Merck, and AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. Hiroki Hara received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and research funding from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo, Eisai, Elevar Therapeutics, GSK, Incyte, Merck Biopharma, MSD, Ono, Pfizer, and Taiho; consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Dainippon Sumitomo, Eli Lilly, MSD, and Ono; and honoraria from Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Eli Lilly, Merck Biopharma, MSD, Ono, Sanofi, Taiho, Takeda, and Yakult outside the submitted work. Satoru Iwasa received research funding from Ono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Pfizer during the conduct of the study; and honoraria from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. Kei Muro received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and research funding from Solasia, Merck Serono, Daiichi Sankyo, Parexel International, Pfizer, MSD, Amgen, Ono, Sanofi, and Taiho; consulting fees from Amgen, Ono, and AstraZeneca; and honoraria from Ono, Sanofi, Taiho, Chugai, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer outside the submitted work. Keiko Minashi received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and research funding from MSD, Mediscience Planning, Merck Biopharma, Astellas, Taiho, and Daiichi Sankyo outside the submitted work. Kensei Yamaguchi received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and grants from Taiho, Yakult Honsha, Sanofi, Ono, and Elli Lilly; and honoraria Taiho, Chugai, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Serono, Takeda, Ono, and Elli Lilly outside the submitted work. Atsushi Ohtsu received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and honorarium from Bristol-Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. Yasuhiro Matsumura is an employee and a stockholder of Ono. Yuko Kitagawa received research funding from Ono and Bristol-Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study; and grants from Takeda, Chugai, Taiho, Yakult Honsha, Asahi Kasei, Otsuka, Ono, Tsumura, EA, Astellas, Toyama Chemical, Medicon, Kaken, Eisai, Otsuka, Teijin, Nihon, and Nippon Covidien; and honoraria from Chugai, Taiho, Asahi Kasei, Otsuka, Shionogi, and Nippon Covidien outside the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Nov;20(11):1506-1517. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30626-6. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31582355 Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in Japanese patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a subgroup analysis of a multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial (ATTRACTION-3).Esophagus. 2021 Jan;18(1):90-99. doi: 10.1007/s10388-020-00794-x. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Esophagus. 2021. PMID: 33170461 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of taxanes following nivolumab in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective chart review of patients in ATTRACTION-3.Esophagus. 2023 Apr;20(2):302-308. doi: 10.1007/s10388-022-00972-z. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Esophagus. 2023. PMID: 36564602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five-year follow-up results from phase II studies of nivolumab in Japanese patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: pooled analysis of the ONO-4538-05 and ONO-4538-06 studies.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan 1;51(1):106-113. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyaa157. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33020837 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging data on nivolumab for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Aug;15(8):845-854. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1948836. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34251958 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy Predictive Molecular Markers in Advanced Gastroesophageal Cancer: MSI and Beyond.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 5;13(7):1715. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071715. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33916348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Targeted Agents Combined With Chemoradiotherapy for the Treatment of Esophageal Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 29;11:621917. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.621917. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34912696 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a machine-learning model to enable treatment selection for neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25669. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11252-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40664895 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 expression and CD8 positive lymphocytes in human neoplasms: A tissue microarray study on 11,838 tumor samples.Cancer Biomark. 2023;36(2):177-191. doi: 10.3233/CBM-220030. Cancer Biomark. 2023. PMID: 36683495 Free PMC article.
-
Absolute lymphocyte count and C-reactive protein-albumin ratio can predict prognosis and adverse events in patients with recurrent esophageal cancer treated with nivolumab therapy.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 14;24(2):257. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13377. eCollection 2022 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35765281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL,Global cancer statistics, et al. GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. 10.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- Shirakawa T, Kato K, Nagashima K, et al. A retrospective study of docetaxel or paclitaxel in patients with advanced or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma who previously received fluoropyrimidine- and platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;74:1207–1215. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2597-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
