Study on the Relationship between the miRNA-centered ceRNA Regulatory Network and Fatigue
- PMID: 33993410
- PMCID: PMC8500871
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-021-01845-3
Study on the Relationship between the miRNA-centered ceRNA Regulatory Network and Fatigue
Abstract
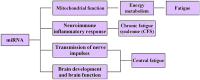
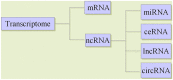
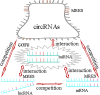
In recent years, the incidence of fatigue has been increasing, and the effective prevention and treatment of fatigue has become an urgent problem. As a result, the genetic research of fatigue has become a hot spot. Transcriptome-level regulation is the key link in the gene regulatory network. The transcriptome includes messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). MRNAs are common research targets in gene expression profiling. Noncoding RNAs, including miRNAs, lncRNAs, circRNAs and so on, have been developed rapidly. Studies have shown that miRNAs are closely related to the occurrence and development of fatigue. MiRNAs can regulate the immune inflammatory reaction in the central nervous system (CNS), regulate the transmission of nerve impulses and gene expression, regulate brain development and brain function, and participate in the occurrence and development of fatigue by regulating mitochondrial function and energy metabolism. LncRNAs can regulate dopaminergic neurons to participate in the occurrence and development of fatigue. This has certain value in the diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). CircRNAs can participate in the occurrence and development of fatigue by regulating the NF-κB pathway, TNF-α and IL-1β. The ceRNA hypothesis posits that in addition to the function of miRNAs in unidirectional regulation, mRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs can regulate gene expression by competitive binding with miRNAs, forming a ceRNA regulatory network with miRNAs. Therefore, we suggest that the miRNA-centered ceRNA regulatory network is closely related to fatigue. At present, there are few studies on fatigue-related ncRNA genes, and most of these limited studies are on miRNAs in ncRNAs. However, there are a few studies on the relationship between lncRNAs, cirRNAs and fatigue. Less research is available on the pathogenesis of fatigue based on the ceRNA regulatory network. Therefore, exploring the complex mechanism of fatigue based on the ceRNA regulatory network is of great significance. In this review, we summarize the relationship between miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs in ncRNAs and fatigue, and focus on exploring the regulatory role of the miRNA-centered ceRNA regulatory network in the occurrence and development of fatigue, in order to gain a comprehensive, in-depth and new understanding of the essence of the fatigue gene regulatory network.
Keywords: Fatigue; MiRNA; NF-κB pathway; ceRNA; circRNA; lncRNA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of the whole coding and non-coding RNA transcriptome expression profiles and construction of the circRNA-lncRNA co-regulated ceRNA network in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Funct Integr Genomics. 2019 Jan;19(1):109-121. doi: 10.1007/s10142-018-0631-y. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30128795
-
High throughput sequencing of whole transcriptome and construct of ceRNA regulatory network in RD cells infected with enterovirus D68.Virol J. 2021 Nov 7;18(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01686-x. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34743709 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Competitive Endogenous RNA Network as Novel Prognostic Markers for Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;11(8):868. doi: 10.3390/genes11080868. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751923 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of ncRNAs as ceRNAs in Gastric Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;12(7):1036. doi: 10.3390/genes12071036. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions Among lncRNAs/circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs in Neuropathic Pain.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):917-931. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00881-y. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32632773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of psoriasis via miR-149-5p/AKT1axis by long noncoding RNA BLACAT1.Skin Res Technol. 2023 May;29(5):e13339. doi: 10.1111/srt.13339. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 37204030 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel intermittent hypoxia-related prognostic lncRNA signature and the ceRNA of lncRNA GSEC/miR-873-3p/EGLN3 regulatory axis in lung adenocarcinoma.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 10;11:e16242. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16242. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37842058 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Differentially Expressed mRNAs, miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs for Xp11 Translocation Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Based on Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;14(3):723. doi: 10.3390/genes14030723. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980995 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying microRNAs Possibly Implicated in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 3;25(17):9551. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179551. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of core genes prognostic for sepsis and construction of a ceRNA regulatory network.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Feb 28;16(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01460-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36855106 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials