Outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastases in patients with malignant melanoma and validation of the melanoma molGPA
- PMID: 33993415
- PMCID: PMC8390419
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-021-02607-8
Outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastases in patients with malignant melanoma and validation of the melanoma molGPA
Abstract
Introduction: Malignant melanoma is the third most common primary in the diagnosis of brain metastases. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a well-established treatment option in limited brain disease. We analyzed outcomes of SRS with a particular focus on the graded prognostic assessment (GPA, melanoma molGPA), prognostic factors, and toxicity.
Methods: We evaluated 173 brain metastases in 83 patients with malignant melanoma. All were treated with SRS median dose of 20 Gy prescribed to the 80 or 100% isodose line between 2002 and 2019. All patients were followed-up regularly, including contrast-enhanced brain imaging as well as clinical examination, initially 6 weeks after treatment, then in quarterly follow-up.
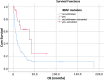
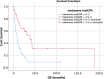
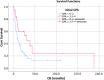
Results: The median age was 61 years (range 27-80); 36 female and 47 male patients were treated. After a median follow-up of 5.7 months, median OS (overall survival) was 9.7 months 95%-KI 4.7-14.7). LC (local control) at 6 months, 12, 24 months was 89%, 86%, and 72%, respectively (median was not reached). Median DBC (distant brain control) was 8.2 months (95%-KI 4.7-11.7). For OS, a KPS ≥ 80%, a positive BRAF mutation status, a small PTV (planning target volume), the absence of extracranial metastases, as well as a GPA and melanoma molGPA > 2 were prognostic factors. In the MVA, a small PTV and a melanoma molGPA > 2 remained significant.
Conclusion: The present survival outcomes support the use of the disease-specific melanoma molGPA as reliable prognostic score. Favorable outcomes for SRS compared to other studies were observed. In the treatment of brain metastases of malignant melanoma patients, a multidisciplinary approach consisting of surgery, SRS, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy should be considered.
Keywords: Brain metastases; GPA; Melanoma; Prognostic factors; Radiosurgery; SRS.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hayat MA Brain Metastases from Primary Tumors Volume Three: Epidemiology, Biology, and Therapy of Melanoma and Other Cancers, ed. M.A. Hayat. 2016 Academic Press. 384.
-
- Sperduto CM, et al. A validation study of a new prognostic index for patients with brain metastases: the graded prognostic assessment. J Neurosurg. 2008;109(Suppl):87–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials