Dupilumab efficacy in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps from SINUS-52 is unaffected by eosinophilic status
- PMID: 33993501
- PMCID: PMC9290136
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14906
Dupilumab efficacy in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps from SINUS-52 is unaffected by eosinophilic status
Abstract
Background: The human monoclonal antibody dupilumab blocks interleukin (IL)-4 andIL-13, key and central drivers of type 2 inflammation. Dupilumab, on background mometasone furoate nasal spray (MFNS), improved outcomes in the phase III SINUS-52 study (NCT02898454) in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP). This posthoc analysis of SINUS-52 examined whether eosinophilic status of CRSwNP was a predictor of dupilumab efficacy.
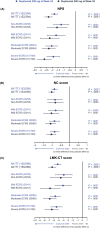
Methods: Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to dupilumab 300 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) until week 52; dupilumab 300 mg q2w until Week 24, then 300 mg every 4 weeks until week 52; or placebo (MFNS) until week 52. Coprimary endpoints were change from baseline in nasal polyps score (NPS), nasal congestion (NC), and Lund-Mackay score assessed by CT (LMK-CT) at week 24. Patients (n = 438) were stratified by eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS) status according to the Japanese Epidemiological Survey of Refractory Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis algorithm.
Results: Dupilumab significantly improved NPS, NC, and LMK-CT scores versus placebo at week 24 in all ECRS subgroups (p < 0.001), with improvements maintained or increased at week 52 (p < 0.001). There was no significant interaction between ECRS subgroup (non-/mild or moderate/severe) and dupilumab treatment effect for all endpoints at weeks 24 and 52 (p > 0.05), except LMK-CT at week 24 (p = 0.0275). Similar results were seen for the secondary endpoints. Dupilumab was well tolerated across all ECRS subgroups.
Conclusion: Dupilumab produced consistent improvement in symptoms of severe CRSwNP irrespective of ECRS status. Therefore, blood eosinophil level may not be a suitable biomarker for dupilumab efficacy in CRSwNP.
Keywords: ENT (rhinitis; biologics; eosinophils; inflammation; nasal polyps); sinusitis.
© 2021 The Authors. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Fujieda S: AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, and Sanofi – advisory board member; Kyorin, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Taiho Pharma – speaker fees. Matsune S: Sanofi – advisory board member; Kyorin, Meiji Seika Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Sanofi, Taiho Pharma, and Tanabe Pharma – speaker fees. Takeno S: Sanofi – advisory board member; Sanofi – speaker fees. Ohta N: Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Sanofi, and Taiho Pharma– speaker fees. Asako M: AstraZeneca, Sanofi, and Taiho Pharma – speaker fees. Bachert C: ALK, ASIT Biotech, AstraZeneca, Intrexon Actobiotics, Novartis, Sanofi, Stallergenes Greer – advisory board member. Inoue T, Takahashi Y, Fujita H, Rowe P, Li Y, Mannent LP: Sanofi – employees, may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. Deniz Y, Ortiz B: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. – employees and shareholders.
Figures

References
-
- Khan A, Vandeplas G, Huynh TMT, et al. The Global Allergy and Asthma European Network (GALEN) rhinosinusitis cohort: a large European cross‐sectional study of chronic rhinosinusitis patients with and without nasal polyps. Rhinology. 2019;57:32‐42. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020;58:1‐464. - PubMed
-
- Klonaris D, Doulaptsi M, Karatzanis A, Velegrakis S, Milioni A, Prokopakis E. Assessing quality of life and burden of disease in chronic rhinosinusitis: a review. Rhinology Online. 2019;2:6‐13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

