A Multilevel Model of the Association Between School Climate and Racial Differences in Academic Outcomes
- PMID: 33994583
- PMCID: PMC8114896
- DOI: 10.1002/pits.22477
A Multilevel Model of the Association Between School Climate and Racial Differences in Academic Outcomes
Abstract
This study examined the relationships between school-level school climate and race differences in student grades, accounting for school sociodemographic composition. We found that schools with more positive school climates had smaller race differences in student self-reported grades. The moderating effect of school climate remained after accounting for the sociodemographic composition of the school and students' own perceptions of climate at their school. This moderating effect was confounded by school grade band (i.e., elementary, middle, or high) since perception of positive school climate was lower in middle and high schools than in elementary schools. Despite the difficulty of disentangling school climate from grade band, the findings suggest school improvement strategies focused on school climate may promote racial equity in academic outcomes. School practitioners' efforts to improve the school climate may also contribute to racial equity in academics.
Keywords: School climate; achievement gap; racial equity; sociodemographic composition.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
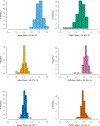

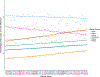
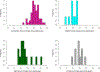
References
-
- Benbenishty R, Astor R, Roziner I, & Wrabel S (2016). Testing the causal links between school climate, school violence, and school academic performance: A cross-lagged panel autoregressive model. Educational Researcher, 45(3), 197–206. 10.3102/0013189X16644603 - DOI
-
- Berkowitz R, Glickman H, Benbenishty R, Ben-Artzi E, Raz T, Lipshtat N, & Astor RA (2015). Compensating, mediating, and moderating effects of school climate on academic achievement gaps in Israel. Teachers College Record, 117, 1–34. EID: 2-s2.0–84938264520
-
- Berkowitz R, Moore H, Astor RA, & Benbenishty R (2016). A research synthesis of the associations between socioeconomic background, inequality, school climate, and academic achievement. Review of Educational Research, 87(2), 425–469. 10.3102/0034654316669821 - DOI
-
- Betancourt H, & López SR (1993). The study of culture, ethnicity, and race in American psychology. American Psychologist, 48(6), 629–637. 10.1037/0003-066X.48.6.629 - DOI
-
- Bond L, Butler H, Thomas L, Carlin J, Glover S, Bowes G, & Patton G (2007). Social and school connectedness in early secondary school as predictors of late teenage substance use, mental health, and academic outcomes. Journal of Adolescent Health, 40(4), 357–e9. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2006.10.013 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
