Neuropeptide Substance P Enhances Inflammation-Mediated Tumor Signaling Pathways and Migration and Proliferation of Head and Neck Cancers
- PMID: 33994734
- PMCID: PMC8119571
- DOI: 10.1007/s13193-020-01210-7
Neuropeptide Substance P Enhances Inflammation-Mediated Tumor Signaling Pathways and Migration and Proliferation of Head and Neck Cancers
Abstract
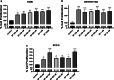
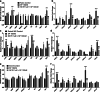
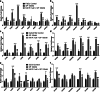
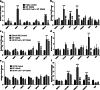
Head and neck cancers (HNC) are extremely aggressive, highly recurrent, and the sixth most common cancer worldwide. Neuropeptide substance P, along with its primary receptor, neurokinin-1 (NK-1R), is overexpressed in HNC and is a central player in inflammation and growth and metastasis of several cancers. However, the precise SP-mediated signaling that promotes HNC progression remains ill defined. Using a panel of HNC lines, in this study, we investigated the effects of SP on proliferation and migration of HNC. Tumor cells were also treated with SP and alterations in inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and their cognate receptors were analyzed by real-time PCR. Furthermore, we investigated the role of SP in inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and matrix metalloproteases that promote tumor invasion. Our results showed that SP significantly increased tumor cell proliferation and migration and induced the expression of several genes that promote tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis which was suppressed by a specific NK1R antagonist L-703606. SP also activated NFκB that was suppressed on inhibiting NK1R. Collectively, our data shows that SP-NK1R-mediated inflammatory signaling comprises an important signaling axis in promoting HNC and may prove to be effective clinical target against HNC cells that are resistant to traditional therapy.
Keywords: Cytokines; Head neck cancer; Inflammation; Neuropeptide; Tumor progression.
© Indian Association of Surgical Oncology 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Substance P and Neurokinin 1 Receptor in Chronic Inflammation and Cancer of the Head and Neck: A Review of the Literature.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 30;19(1):375. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010375. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35010633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential in vitro therapeutic effects of targeting SP/NK1R system in cervical cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1067-1076. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06928-3. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34766230
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote head and neck cancer progression through Periostin-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin.Cancer Sci. 2018 Mar;109(3):688-698. doi: 10.1111/cas.13479. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29284199 Free PMC article.
-
Differential consequences of neurokinin receptor 1 and 2 antagonists in metastatic breast carcinoma cells; Effects independent of Substance P.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:263-270. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.013. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30223097
-
New insight into the role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system in breast cancer progression and its crosstalk with microRNAs.Clin Genet. 2020 Oct;98(4):322-330. doi: 10.1111/cge.13750. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Clin Genet. 2020. PMID: 32266968 Review.
Cited by
-
Substance P and Neurokinin 1 Receptor in Chronic Inflammation and Cancer of the Head and Neck: A Review of the Literature.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 30;19(1):375. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010375. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35010633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential in vitro therapeutic effects of targeting SP/NK1R system in cervical cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1067-1076. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06928-3. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34766230
-
Sensory neurotransmission and pain in solid tumor progression.Trends Cancer. 2025 Apr;11(4):309-320. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2025.01.003. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Trends Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39884880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroscience of cancer: Focus on neuropeptidergic systems.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 May;15(5):2323-2350. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.03.025. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40487638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conjugated Bile Acids Promote Lymphangiogenesis by Modulation of the Reactive Oxygen Species-p90RSK-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 3 Pathway.Cells. 2023 Feb 6;12(4):526. doi: 10.3390/cells12040526. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
