Altered Temporal Dynamics of Brain Activity in Multiple-Frequency Bands in Non-Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Inactive Disease
- PMID: 33994788
- PMCID: PMC8113012
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S292302
Altered Temporal Dynamics of Brain Activity in Multiple-Frequency Bands in Non-Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Inactive Disease
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we seek to investigate dynamic changes of brain activity in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (non-NPSLE) patients with inactive disease.
Patients and methods: Thirty-one non-NPSLE patients with inactive disease and 20 matched healthy controls underwent the blood oxygenation level-dependent fMRI examination. Dynamic regional homogeneity (ReHo) and fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (fALFF) were used to analyze the brain activity in typical band (0.01-0.08 Hz), slow-4 (0.027-0.073 Hz) and slow-5 (0.01-0.027 Hz). Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to correlate dynamic regional homogeneity (dReHo) and dynamic fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (dfALFF) values for clusters of voxels where significant group differences were found with clinical variables in non-NPSLE patients with inactive disease.
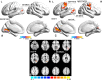
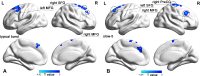
Results: In typical band, non-NPSLE patients showed increased dReHo in left middle occipital gyrus (MOG) compared to healthy controls. Meanwhile, patients showed decreased dfALFF in right superior frontal gyrus (SFG) and bilateral middle frontal gyrus (MFG) in typical band. In slow-4, increased dReHo in left MOG was found in non-NPSLE patients. In slow-5, non-NPSLE patients showed increased dReHo in left MOG, left calcarine fissure and surrounding cortex, right precentral gyrus (PreCG) and left postcentral gyrus (PoCG). Meanwhile, non-NPSLE patients showed decreased dfALFF in left SFG, right MFG, and right PreCG in slow-5. Moreover, the glucocorticoid dose showed significantly negative correlations with dReHo values in right PreCG in slow-5, left PoCG in slow-5, and left MOG in typical band.
Conclusion: dReHo and dfALFF abnormalities in different frequency bands may be the key characteristics in the pathogenesis mechanism of non-NPSLE.
Keywords: dynamic fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; dynamic regional homogeneity; frequency bands; non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus; resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Abnormal amplitude of low frequency fluctuation and functional connectivity in non-neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a resting-state fMRI study.Neuroradiology. 2019 Mar;61(3):331-340. doi: 10.1007/s00234-018-2138-6. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Neuroradiology. 2019. PMID: 30637462
-
Alterations of spontaneous brain activity in systematic lupus erythematosus patients without neuropsychiatric symptoms: A resting-functional MRI study.Lupus. 2021 Oct;30(11):1781-1789. doi: 10.1177/09612033211033984. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 34620007
-
Altered Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuations in Inactive Patients with Nonneuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Neural Plast. 2019 Nov 25;2019:9408612. doi: 10.1155/2019/9408612. eCollection 2019. Neural Plast. 2019. PMID: 31885539 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted resting-state interhemispheric functional connectivity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and without neuropsychiatric lupus.Neuroradiology. 2022 Jan;64(1):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s00234-021-02750-7. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 34379142
-
Alterations of regional spontaneous brain activity in obsessive-compulsive disorders: A meta-analysis.J Psychiatr Res. 2023 Sep;165:325-335. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.07.036. Epub 2023 Aug 2. J Psychiatr Res. 2023. PMID: 37573797 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic changes of amplitude of low-frequency in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with cognitive impairment.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 23;16:929383. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.929383. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36081656 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic local metrics changes in patients with toothache: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 12;13:1077432. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1077432. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36578304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin O, Kaul A, Smith TO, et al. Comparison of structural magnetic resonance imaging findings between neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Pract Res. 2017;2(1–11):205990211666305. doi:10.1177/2059902116663058 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

