Cyclophilin A Plays Potential Roles in a Rat Model of Asthma and Suppression of Immune Response
- PMID: 33994799
- PMCID: PMC8114824
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S308938
Cyclophilin A Plays Potential Roles in a Rat Model of Asthma and Suppression of Immune Response
Abstract
Purpose: Cyclophilin A (CypA) inhibits CD4+ T cell signal transduction via interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (Itk), a tyrosine kinase required for T helper (Th) 2 cells function. Furthermore, mice with CypA silencing developed allergic diseases associated with increased Th2 cytokines production. CD4+ T cells with a Th2-cytokine pattern have been demonstrated to have a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of asthma. However, the effects of CypA in regulating immunity in asthma and in relieving asthmatic symptoms in vivo are entirely unknown.
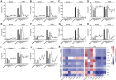
Methods: Recombinant CypA protein (rCypA) was generated and purified. Ovalbumin (OVA)-challenged asthmatic rats model and acetylcholine chloride (ACh)-induced contraction of tracheal spirals were established. The pulmonary resistance (RL) value of asthmatic rats in vivo and the isometric tension of tracheal spirals ex vivo were recorded by MFLab 3.01 software. The levels of Th1 and Th2 cytokines and the quantities of immunoglobulin (IgA, IgG, IgM and IgE) in the supernatants of rat spleen lymphocytes were detected and analysed by bio-plex Suspension Array System and ELISA, respectively. CD4+ T cells were separated by MicroBeads, and the levels of interleukin (IL)-4 and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) were detected by ELISA.
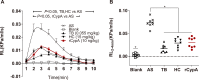
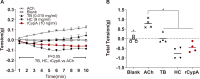
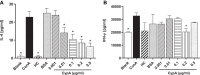
Results: rCypA (10 ng/kg) significantly reduced RL within 2-7 min in OVA-challenged asthmatic rats in vivo, and there were no significant differences compared with terbutaline (TB) and hydrocortisone (HC). Furthermore, rCypA (10 ng/mL) significantly reduced the isometric tension in the ACh-induced contraction of the tracheal spiral ex vivo, and the effect of rCypA was better than that of TB. Additionally, rCypA suppressed the secretion of both Th1 and Th2 cytokines, and the suppressive effects of rCypA were stronger than those of HC, especially on Th2 cytokines.
Conclusion: These findings indicate that CypA may serve as a potential novel therapeutic strategy for asthma.
Keywords: Th2 cytokines; asthma; cyclophilin A; immunoregulation.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PARP inhibition by olaparib or gene knockout blocks asthma-like manifestation in mice by modulating CD4(+) T cell function.J Transl Med. 2015 Jul 14;13:225. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0583-0. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26169874 Free PMC article.
-
[The evolvement of Th1/Th2 imbalance accommodates to the progress of airway inflammation in asthmatic subjects and rat model].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Sep 2;84(17):1440-4. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15500739 Chinese.
-
Yan-Hou-Qing formula attenuates allergic airway inflammation via up-regulation of Treg and suppressing Th2 responses in Ovalbumin-induced asthmatic mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 1;231:275-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.038. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30496840
-
Effects of histamine on Th1/Th2 cytokine balance.Int Immunopharmacol. 2003 Jul;3(7):909-20. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5769(02)00235-7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12810348 Review.
-
[A role for T-helper type 1 and type 2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of various human diseases].Rinsho Byori. 1998 Sep;46(9):915-21. Rinsho Byori. 1998. PMID: 9800477 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Stigmasterol alleviates airway inflammation in OVA-induced asthmatic mice via inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad2 and IL-17A signaling pathways.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 4;16(7):6478-6487. doi: 10.18632/aging.205716. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38579176 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the mechanism and efficacy of natural products on treating the asthma: Current insights from traditional medicine to modern drug discovery.Heliyon. 2024 May 28;10(11):e32008. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32008. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38882318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma(2020). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention; 2020. Available from: www.ginasthma.org. Accessed April8, 2021.
-
- Soriano JB, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(9):691–706. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

