Normal Basal Epithelial Cells Stimulate the Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cell RM-1 by TGF-β1/STAT3 Axis in vitro
- PMID: 33994809
- PMCID: PMC8114913
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S303122
Normal Basal Epithelial Cells Stimulate the Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cell RM-1 by TGF-β1/STAT3 Axis in vitro
Abstract
Aim: Basal epithelial cells are absent in distant prostate cancer. This study aimed to investigate whether basal epithelial cells could suppress migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells to become a new treatment strategy for prostate cancer.
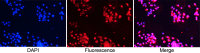
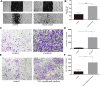
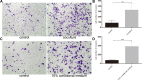
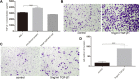
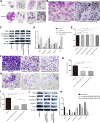
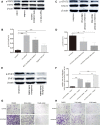
Main methods: Basal epithelial cells were identified by immunofluorescence with anti-p63. Wound healing assays or transwell assays were used to explore the effects of basal epithelial cells, TGF-β1, SB431542 (inhibitor of TGF-β type I receptor) or stattic (inhibitor of phosphorylated STAT3) on migration or invasion of mouse prostate cancer cell (RM-1). Concentration of TGF-β1 was measured by ELISA assay. HE staining was used to investigate cell morphology. Immunocytochemistry with anti-p63 was used to identify basal epithelial cells. Levels of STAT3, p-STAT3 (Ser727) and proteins associated with EMT were measured with Western blot assay. Cell proliferation was measured with MTT or CCK8 assay.
Results: Normal basal epithelial cells acquired from mouse prostate were specific to anti-p63 and more than 90%. Basal epithelial cells and RM-1 could both secrete TGF-β1. Basal epithelial cells and TGF-β1 promoted the migration and invasion of RM-1 through changing the cell morphology and up-regulating expression of ZEB1, N-cadherin, vimentin, snail and p-STAT3 (Ser727), at the same time down-regulating E-cadherin of RM-1. SB431542 strongly suppressed migration, invasion as well as the expressions of EMT relevant proteins and p-STAT3 (Ser727) of co-cultured RM-1. In addition, stattic suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion of non-treated RM-1 and co-cultured RM-1.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that normal basal epithelial cells might stimulate the migration and invasion of RM-1 by TGF-β1/STAT3 axis which could be suppressed by inhibitor of TGF-β receptor and inhibitor of p-STAT3. So, basal epithelial cells might not become a treatment strategy for prostate cancer, but our results could provide some researching references for other diseases which include basal epithelial cells such as prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, prostatic hyperplasia, cervical cancer, or urinary bladder cancer.
Keywords: RM-1; STAT3; TGF-β1; invasion; migration; normal basal epithelial cells.
© 2021 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

