Gastric floating tablet improves the bioavailability and reduces the hypokalemia effect of gossypol in vivo
- PMID: 33994825
- PMCID: PMC8093546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.03.001
Gastric floating tablet improves the bioavailability and reduces the hypokalemia effect of gossypol in vivo
Abstract
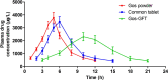
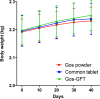
Gossypol (Gos) is a natural polyphenolic compound that has shown a number of valuable biological properties such as antifertility, antioxidation, and antitumor activities. However, the clinical application of Gos has been hindered by its notable adverse effects such as hypokalemia, hemolytic anemia, and so on. Using sustained-release dosage form provides a hopeful solution to this problem. In this study, a gastric floating tablet for sustained-release of Gos (Gos-GFT) was developed using polyvinylpyrrolidone, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, lactose, sodium bicarbonate, and magnesium stearate. Gos-GFT had an average weight of around 200 mg with a drug content percentage of around 13.66%. The physicochemical properties of Gos-GFT satisfied the pharmacopoeial requirements for tablets. Gos-GFT was able to float in an acidic medium and had a sustained drug release for over 12 h. In vivo studies showed that the relative bioavailability of Gos-GFT, as compared with Gos powders, was larger than that of a non-gastric floating tablet which was a dosage form used for comparison with Gos-GFT. Furthermore, compared with the Gos powders and the non-gastric floating Gos tablets, Gos-GFT could prolong the in vivo action time of Gos, and significantly relieve hypokalemia which is a major adverse effect of Gos. These properties made Gos-GFT a promising Gos preparation that warrants further investigation for more extensive clinical applications of this natural compound.
Keywords: Adverse effect; Bioavailability; Gastric floating tablet; Gossypol; Pharmacokinetics; Sustained release.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gastric floating sustained-release tablet for dihydromyricetin: Development, characterization, and pharmacokinetics study.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Nov;27(7):1000-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31997907 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of 3D printing technologies and compressed tablets for preparation of riboflavin floating tablet-in-device (TiD) systems.Int J Pharm. 2018 Oct 5;549(1-2):370-379. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.08.011. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30107218
-
Floating tablets for controlled release of ofloxacin via compression coating of hydroxypropyl cellulose combined with effervescent agent.Int J Pharm. 2015 Jul 15;489(1-2):210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.05.007. Epub 2015 May 5. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25956047
-
Design and optimization of gastro-floating sustained-release tablet of pregabalin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation.Int J Pharm. 2018 Jul 10;545(1-2):37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.011. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29649518
-
Gossypol: a potential antifertility agent for males.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:329-60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.001553. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984. PMID: 6375548 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of floating formulations and antiulcer activity of Desmostachya bipinnata.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 21;25(3):44. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02745-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38383866
-
A Comprehensive Review of Challenges in Oral Drug Delivery Systems and Recent Advancements in Innovative Design Strategies.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(5):360-376. doi: 10.2174/0113816128338560240923073357. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39390835 Review.
-
Polymeric Excipients in the Technology of Floating Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 12;14(12):2779. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122779. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclic RGD-Decorated Liposomal Gossypol AT-101 Targeting for Enhanced Antitumor Effect.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jan 14;17:227-244. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S341824. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35068931 Free PMC article.
-
Strategic developments in the drug delivery of natural product dihydromyricetin: applications, prospects, and challenges.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):3052-3070. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2125601. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36146939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

