Evolving deep convolutional neutral network by hybrid sine-cosine and extreme learning machine for real-time COVID19 diagnosis from X-ray images
- PMID: 33994846
- PMCID: PMC8107782
- DOI: 10.1007/s00500-021-05839-6
Evolving deep convolutional neutral network by hybrid sine-cosine and extreme learning machine for real-time COVID19 diagnosis from X-ray images
Abstract
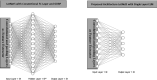
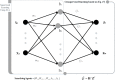
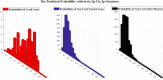
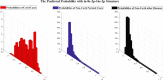
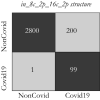
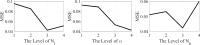
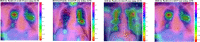
The COVID19 pandemic globally and significantly has affected the life and health of many communities. The early detection of infected patients is effective in fighting COVID19. Using radiology (X-Ray) images is, perhaps, the fastest way to diagnose the patients. Thereby, deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) can be considered as applicable tools to diagnose COVID19 positive cases. Due to the complicated architecture of a deep CNN, its real-time training and testing become a challenging problem. This paper proposes using the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) instead of the last fully connected layer to address this deficiency. However, the parameters' stochastic tuning of ELM's supervised section causes the final model unreliability. Therefore, to cope with this problem and maintain network reliability, the sine-cosine algorithm was utilized to tune the ELM's parameters. The designed network is then benchmarked on the COVID-Xray-5k dataset, and the results are verified by a comparative study with canonical deep CNN, ELM optimized by cuckoo search, ELM optimized by genetic algorithm, and ELM optimized by whale optimization algorithm. The proposed approach outperforms comparative benchmarks with a final accuracy of 98.83% on the COVID-Xray-5k dataset, leading to a relative error reduction of 2.33% compared to a canonical deep CNN. Even more critical, the designed network's training time is only 0.9421 ms and the overall detection test time for 3100 images is 2.721 s.
Keywords: COVID19; Chest X-ray images; Deep convolutional neural networks; Extreme learning machine; Sine–cosine algorithm.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures













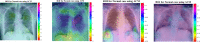
Similar articles
-
Real‑time COVID-19 diagnosis from X-Ray images using deep CNN and extreme learning machines stabilized by chimp optimization algorithm.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021 Jul;68:102764. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102764. Epub 2021 May 11. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2021. PMID: 33995562 Free PMC article.
-
Improved deep convolutional neural networks using chimp optimization algorithm for Covid19 diagnosis from the X-ray images.Expert Syst Appl. 2023 Mar 1;213:119206. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119206. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Expert Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 36348736 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Diffuse Airspace Opacities Diagnosis from Chest X-Ray Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Fine-Tuned by Whale Optimizer.Wirel Pers Commun. 2022;124(2):1355-1374. doi: 10.1007/s11277-021-09410-2. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Wirel Pers Commun. 2022. PMID: 34873379 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of COVID19 from X-ray images using multiscale Deep Convolutional Neural Network.Appl Soft Comput. 2022 Apr;119:108610. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108610. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Appl Soft Comput. 2022. PMID: 35185439 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fitness dependent optimizer with neural networks for COVID-19 patients.Comput Methods Programs Biomed Update. 2023;3:100090. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpbup.2022.100090. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Comput Methods Programs Biomed Update. 2023. PMID: 36591535 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of Marine Mammals Using the Trained Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network with the Whale Algorithm Developed with the Fuzzy System.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Oct 18;2022:3216400. doi: 10.1155/2022/3216400. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36304739 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving deep convolutional neural networks by IP-based marine predator algorithm for COVID-19 diagnosis using chest CT scans.J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2022 May 24:1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12652-022-03901-1. Online ahead of print. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2022. PMID: 35646192 Free PMC article.
-
An enhanced and efficient approach for feature selection for chronic human disease prediction: A breast cancer study.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 28;10(5):e26799. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26799. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38463826 Free PMC article.
-
BO-ALLCNN: Bayesian-Based Optimized CNN for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Detection in Microscopic Blood Smear Images.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 24;22(15):5520. doi: 10.3390/s22155520. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35898023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abualigah LM, Khader AT, Al-Betar MA, Alomari OA. Text feature selection with a robust weight scheme and dynamic dimension reduction to text document clustering. Expert Syst Appl. 2017;84:24–36. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.05.002. - DOI
-
- Abualigah L, Diabat A, Mirjalili S, Abd Elaziz M, Gandomi AH. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2021;376:113609. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113609. - DOI
-
- Alabool H, Alarabiat D, Abualigah L et al (2020) Artificial intelligence techniques for containment COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. 10.21203/rs.3.rs-30432/v1
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
