Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Inhibitors suppress the Tumor-initiating properties of a CD44+CD133+ subpopulation of Caco-2 cells
- PMID: 33994850
- PMCID: PMC8120464
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.58612
Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Inhibitors suppress the Tumor-initiating properties of a CD44+CD133+ subpopulation of Caco-2 cells
Abstract
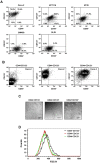
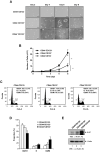
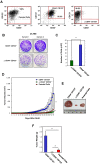
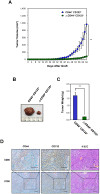
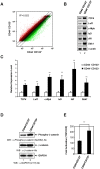
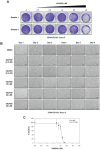
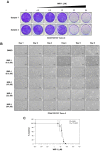
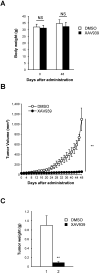
Tumor-initiating cells or cancer stem cells are a subset of cancer cells that have tumorigenic potential in human cancer. Although several markers have been proposed to distinguish tumor-initiating cells from colorectal cancer cells, little is known about how this subpopulation contributes to tumorigenesis. Here, we characterized a tumor-initiating cell subpopulation from Caco-2 colorectal cancer cells. Based on the findings that Caco-2 cell subpopulations express different cell surface markers, we were able to discriminate three main fractions, CD44-CD133-, CD44-CD133+, and CD44+CD133+ subsets, and characterized their biochemical and tumorigenic properties. Our results show that CD44+CD133+ cells possessed an unusual capacity to proliferate and could form tumors when transplanted into NSG mice. Additionally, primary tumors grown from CD44+CD133+ Caco-2 cells contained mixed populations of CD44+CD133+ and non-CD44+CD133+ Caco-2 cells, indicating that the full phenotypic heterogeneity of the parental Caco-2 cells was re-created. Notably, only the CD44+CD133+ subset of Caco-2-derived primary tumors had tumorigenic potential in NSG mice, and the tumor growth of CD44+CD133+ cells was faster in secondary xenografts than in primary transplants. Gene expression analysis revealed that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was over-activated in CD44+CD133+ cells, and the growth and tumorigenic potential of this subpopulation were significantly suppressed by small-molecule Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitors. Our findings suggest that the CD44+CD133+ subpopulation from Caco-2 cells was highly enriched in tumorigenic cells and will be useful for investigating the mechanisms leading to human colorectal cancer development.
Keywords: CD133; CD44; Caco-2; IWR-1; Tumor-initiating cells; Tumorigenic potential; Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitor; XAV939.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020. - PubMed
-
- Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ. Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:476–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

