MUC3A induces PD-L1 and reduces tyrosine kinase inhibitors effects in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 33994852
- PMCID: PMC8120466
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.57964
MUC3A induces PD-L1 and reduces tyrosine kinase inhibitors effects in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
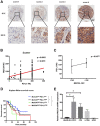
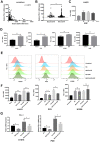
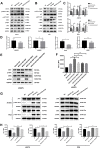
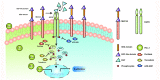
The immune checkpoint ligand programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and the transmembrane mucin (MUC) 3A are upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), contributing to the aggressive pathogenesis and poor prognosis. Here, we report that knocking down the oncogenic MUC3A suppresses the PD-L1 expression in NSCLC cells. MUC3A is a potent regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) stability, and MUC3A deficiency downregulates the activation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways, which subsequently reduces the expression of PD-L1. Furthermore, knockdown of MUC3A and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells play a synergistic effect on inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis in vitro. In the BALB/c nude mice xenograft model, MUC3A deficiency enhances EGFR-mutated NSCLC sensitivity to TKIs. Our study shows that transmembrane mucin MUC3A induces PD-L1, thereby promoting immune escape in NSCLC, while downregulation of MUC3A enhances TKIs effects in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. These findings offer insights into the design of novel combination treatment for NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR; MUC3A; PD-L1.; non-small cell lung cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The canonical TGF-β/Smad signalling pathway is involved in PD-L1-induced primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer.Respir Res. 2019 Jul 22;20(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1137-4. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31331328 Free PMC article.
-
ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3392-3416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537094 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation.J Thorac Oncol. 2015 Jun;10(6):910-23. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000500. J Thorac Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25658629
-
Role of the dynamic tumor microenvironment in controversies regarding immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR mutations.Mol Cancer. 2019 Sep 16;18(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1062-7. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31526368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted roles of mucins family in lung cancer: from prognostic biomarkers to promising targets.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1608140. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1608140. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40655139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qingfei Jiedu decoction inhibits PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology analysis, molecular docking and experimental verification.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:897966. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.897966. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091822 Free PMC article.
-
MUC3A promotes the progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the MAPK/ERK pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 8;16(1):493. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02199-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40198406 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of DNAJB1-PRKACA oncogene suppresses the differentiation potential of liver progenitor organoids towards a hepatocyte lineage.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11028-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670531 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Expression in Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors/Pituitary Adenomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 8;15(18):4471. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184471. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K, Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC. et al. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:895–903. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee SJ, Jang BC, Lee SW, Yang YI, Suh SI, Park YM. et al. Interferon regulatory factor-1 is prerequisite to the constitutive expression and IFN-gamma-induced upregulation of B7-H1 (CD274) FEBS Lett. 2006;580:755–62. - PubMed
-
- Zhang N, Zeng Y, Du W, Zhu J, Shen D, Liu Z. et al. The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 2016;49:1360–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

