Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation
- PMID: 33994855
- PMCID: PMC8120470
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.58888
Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation
Abstract
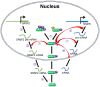
Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 2 (SRSF2) is a splicing factor that is widely expressed in a variety of mammalian cell types. Increasing evidence has confirmed that SRSF2 plays vital roles in a number of biological and pathological processes. Therefore, it is important to understand how its expression is regulated, and how it regulates the expression of its target genes. Recently, we found that SRSF2 expression could be upregulated by herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) infection, and that altered SRSF2 expression, in turn, epigenetically regulates the transcription of HSV-1 genes. Further studies on T cell exhaustion demonstrated that upregulated SRSF2 in exhausted T cells elevated the levels of multiple immune checkpoint molecules by associating with the acyl-transferases, P300 and CBP, and by altering histone modification near the transcription start sites of these genes, thereby influencing signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 binding to these gene promoters. These findings suggest that SRSF2 acts as an important sensor and effector during disease progression. Here, we discuss the molecules that regulate SRSF2 gene expression and their associated mechanisms, and the mechanisms via which SRSF2 regulates the expression of target genes, thus providing novel insights into the central role of SRSF2 in gene regulation.
Keywords: SC35; SRSF2; gene regulation; mRNA stability.; splicing; transcription.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

