ARHGAP25 Inhibits Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Growth by Suppressing Glycolysis via AKT/mTOR Pathway
- PMID: 33994864
- PMCID: PMC8120455
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.55919
ARHGAP25 Inhibits Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Growth by Suppressing Glycolysis via AKT/mTOR Pathway
Abstract
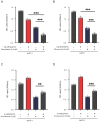
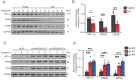
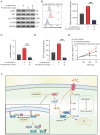
Increasing evidence reveals that the Rho GTPase-activating protein is a crucial negative regulator of Rho family GTPase involved in tumorigenesis. The Rho GTPase-activating protein 25 (ARHGAP25) has been shown to specifically inactivate the Rho family GTPase Rac1, which plays an important role in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) progression. Therefore, here we aimed to clarify the expression and functional role of ARHGAP25 in PAAD. The ARHGAP25 expression was lower in PAAD tissues than that in normal pancreatic tissues based on bioinformatics analysis and immunohistochemistry staining. Overexpression of ARHGAP25 inhibited cell growth of AsPC-1 human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro, while opposite results were observed in BxPC-3 human pancreatic cancer cells with ARHGAP25 knockdown. Consistently, in vivo tumorigenicity assays also confirmed that ARHGAP25 overexpression suppressed tumor growth. Mechanically, overexpression of ARHGAP25 inactivated AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by regulating Rac1/PAK1 signaling, which was in line with the results from the Gene set enrichment analysis on The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset. Furthermore, we found that ARHGAP25 reduced HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis in PAAD cells. Treatment with PF-04691502, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, hampered the increased cell growth and glycolysis due to ARHGAP25 knockdown in PAAD cells. Altogether, these results conclude that ARHGAP25 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, which might provide a therapeutic target for PAAD.
Keywords: AKT/mTOR signaling; ARHGAP25; glycolysis; pancreatic adenocarcinoma; proliferation..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ. Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:690–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

