MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 33994867
- PMCID: PMC8120467
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.59588
MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
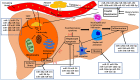
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), or, more accurately, metabolic associated fatty liver disease, accounts for a large proportion of chronic liver disorders worldwide and is closely associated with other conditions such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. NAFLD ranges from simple steatosis to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and can progress to cirrhosis and, eventually, also hepatocellular carcinoma. The morbidity and mortality associated with NAFLD are increasing rapidly year on year. Consequently, there is an urgent need to understand the etiology and pathogenesis of NAFLD and identify effective therapeutic targets. MicroRNAs (miRNAs), important epigenetic factors, have recently been proposed to participate in NAFLD pathogenesis. Here, we review the roles of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, hepatic stellate cell activation, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress, key factors that contribute to the occurrence and progression of NAFLD. Additionally, we summarize the role of miRNA-enriched extracellular vesicles in NAFLD. These miRNAs may comprise suitable therapeutic targets for the treatment of this condition.
Keywords: NAFLD; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Pathogenesis; miRNAs.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M. et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E. et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69(6):2672–2682. - PubMed
-
- Petroni ML, Brodosi L, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G. Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMJ. 2021;372:m4747. - PubMed
-
- Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2013;57(2):840–847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

