Decoding Covert Speech From EEG-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 33994922
- PMCID: PMC8116487
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.642251
Decoding Covert Speech From EEG-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
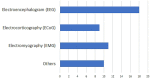
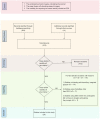
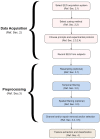
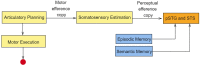
Over the past decade, many researchers have come up with different implementations of systems for decoding covert or imagined speech from EEG (electroencephalogram). They differ from each other in several aspects, from data acquisition to machine learning algorithms, due to which, a comparison between different implementations is often difficult. This review article puts together all the relevant works published in the last decade on decoding imagined speech from EEG into a single framework. Every important aspect of designing such a system, such as selection of words to be imagined, number of electrodes to be recorded, temporal and spatial filtering, feature extraction and classifier are reviewed. This helps a researcher to compare the relative merits and demerits of the different approaches and choose the one that is most optimal. Speech being the most natural form of communication which human beings acquire even without formal education, imagined speech is an ideal choice of prompt for evoking brain activity patterns for a BCI (brain-computer interface) system, although the research on developing real-time (online) speech imagery based BCI systems is still in its infancy. Covert speech based BCI can help people with disabilities to improve their quality of life. It can also be used for covert communication in environments that do not support vocal communication. This paper also discusses some future directions, which will aid the deployment of speech imagery based BCI for practical applications, rather than only for laboratory experiments.
Keywords: brain-computer interfaces (BCI); covert speech; electroencephalogram (EEG); imagined speech; inner speech; neurorehabilitation; speech imagery.
Copyright © 2021 Panachakel and Ramakrishnan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdulkader S. N., Atia A., Mostafa M.-S. M. (2015). Brain computer interfacing: applications and challenges. Egypt. Inform. J. 16, 213–230. 10.1016/j.eij.2015.06.002 - DOI
-
- Agarap A. F. (2018). Deep learning using rectified linear units (ReLU). arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.08375.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

