Decoding Multiple Sound-Categories in the Auditory Cortex by Neural Networks: An fNIRS Study
- PMID: 33994978
- PMCID: PMC8113416
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.636191
Decoding Multiple Sound-Categories in the Auditory Cortex by Neural Networks: An fNIRS Study
Abstract
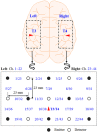
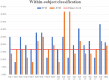
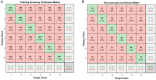
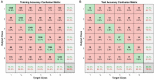
This study aims to decode the hemodynamic responses (HRs) evoked by multiple sound-categories using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS). The six different sounds were given as stimuli (English, non-English, annoying, nature, music, and gunshot). The oxy-hemoglobin (HbO) concentration changes are measured in both hemispheres of the auditory cortex while 18 healthy subjects listen to 10-s blocks of six sound-categories. Long short-term memory (LSTM) networks were used as a classifier. The classification accuracy was 20.38 ± 4.63% with six class classification. Though LSTM networks' performance was a little higher than chance levels, it is noteworthy that we could classify the data subject-wise without feature selections.
Keywords: auditory cortex; decoding; deep learning; functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS); long short-term memories (LSTMs).
Copyright © 2021 Yoo, Santosa, Kim and Hong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Decoding four different sound-categories in the auditory cortex using functional near-infrared spectroscopy.Hear Res. 2016 Mar;333:157-166. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.01.009. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 26828741
-
Classification of somatosensory cortex activities using fNIRS.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Aug 30;333:225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.06.034. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28668280
-
A hybrid BCI based on EEG and fNIRS signals improves the performance of decoding motor imagery of both force and speed of hand clenching.J Neural Eng. 2015 Jun;12(3):036004. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/12/3/036004. Epub 2015 Apr 2. J Neural Eng. 2015. PMID: 25834118
-
Deep Learning-Based Multilevel Classification of Alzheimer's Disease Using Non-invasive Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 26;14:810125. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.810125. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35557842 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Signal Analysis and Advances in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signal: A Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2016 Jun 9;10:261. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00261. eCollection 2016. Front Hum Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27375458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
fNIRS-Based Upper Limb Motion Intention Recognition Using an Artificial Neural Network for Transhumeral Amputees.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 18;22(3):726. doi: 10.3390/s22030726. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161473 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of functional activation responses from the auditory cortex derived using multi-distance frequency domain and continuous wave near-infrared spectroscopy.Neurophotonics. 2021 Oct;8(4):045004. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.8.4.045004. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Neurophotonics. 2021. PMID: 34926716 Free PMC article.
-
Natural sounds can be reconstructed from human neuroimaging data using deep neural network representation.PLoS Biol. 2025 Jul 23;23(7):e3003293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003293. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40700446 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning in fNIRS: a review.Neurophotonics. 2022 Oct;9(4):041411. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.4.041411. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35874933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Noise Filtering in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signals Using Wavelet Transform and Long-Short Term Memory Networks.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jun 4;10(6):685. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060685. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370616 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

