Increased MANF Expression in the Inferior Temporal Gyrus in Patients With Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 33994992
- PMCID: PMC8117094
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.639318
Increased MANF Expression in the Inferior Temporal Gyrus in Patients With Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
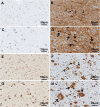
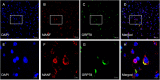
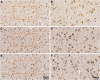
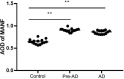
Alzheimer disease (AD) is an aging-related disorder linked to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The main pathologic feature of AD is the presence of extracellular senile plaques and intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain. In neurodegenerative diseases, the unfolded protein response (UPR) induced by ER stress ensures cell survival. Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) protects against ER stress and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of AD. MANF is expressed in neurons of the brain and spinal cord. However, there have been no investigations on MANF expression in the brain of AD patients. This was addressed in the present study by immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and quantitative analyses of postmortem brain specimens. We examined the localization and expression levels of MANF in the inferior temporal gyrus of the cortex (ITGC) in AD patients (n = 5), preclinical (pre-)AD patients (n = 5), and age-matched non-dementia controls (n = 5) by double immunofluorescence labeling with antibodies against the neuron-specific nuclear protein neuronal nuclei (NeuN), ER chaperone protein 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78), and MANF. The results showed that MANF was mainly expressed in neurons of the ITGC in all 3 groups; However, the number of MANF-positive neurons was significantly higher in pre-AD (Braak stage III/IV) and AD (Braak stage V/VI) patients than that in the control group. Thus, MANF is overexpressed in AD and pre-AD, suggesting that it can serve as a diagnostic marker for early stage disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; MANF; cerebral cortex; endoplasmic reticulum stress; hyperphosphorylated tau; senile plaque.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Qi, Fang, Zhou, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) protects against Aβ toxicity via attenuating Aβ-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Feb 13;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1429-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30760285 Free PMC article.
-
The cytoprotective protein MANF promotes neuronal survival independently from its role as a GRP78 cofactor.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100295. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100295. Epub 2021 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33460650 Free PMC article.
-
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF), a new player in endoplasmic reticulum diseases: structure, biology, and therapeutic roles.Transl Res. 2017 Oct;188:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28719799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) expression offers protection against alcohol neurotoxicity.J Neurochem. 2023 Sep;166(6):943-959. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15921. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Neurochem. 2023. PMID: 37507360 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles for Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (MANF) in Pancreatic Beta Cells and Diabetes.Front Physiol. 2018 Oct 16;9:1457. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01457. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30386256 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloidogenesis and Neurotrophic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease: Do They have a Common Regulating Pathway?Cells. 2022 Oct 12;11(20):3201. doi: 10.3390/cells11203201. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the Landscape of MANF Research: A Scientometric Journey with CiteSpace Analysis.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):3897-3913. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01412-x. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37751132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting cognitive dysfunction and regional hubs using Braak staging amyloid-beta biomarkers and machine learning.Brain Inform. 2023 Dec 3;10(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40708-023-00213-8. Brain Inform. 2023. PMID: 38043122 Free PMC article.
-
Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (MANF): An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Disorders.Cells. 2023 Mar 28;12(7):1032. doi: 10.3390/cells12071032. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor (MANF) contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Oct 18;19(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00771-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39425207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrieta A., Blackwood E. A., Stauffer W. T., Santo Domingo M., Bilal A. S., Thuerauf D. J., et al. (2020). Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor is an ER-resident chaperone that protects against reductive stress in the heart. J. Biol. Chem. 295 7566–7583. 10.1074/jbc.ra120.013345 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

