Fyn Kinase-Mediated PKCδ Y311 Phosphorylation Induces Dopaminergic Degeneration in Cell Culture and Animal Models: Implications for the Identification of a New Pharmacological Target for Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 33995031
- PMCID: PMC8113680
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.631375
Fyn Kinase-Mediated PKCδ Y311 Phosphorylation Induces Dopaminergic Degeneration in Cell Culture and Animal Models: Implications for the Identification of a New Pharmacological Target for Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
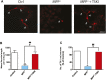
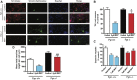
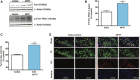
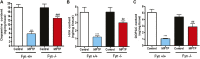
Oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis are some of the key etiological factors responsible for dopamin(DA)ergic degeneration during Parkinson's disease (PD), yet the downstream molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegeneration are largely unknown. Recently, a genome-wide association study revealed the FYN gene to be associated with PD, suggesting that Fyn kinase could be a pharmacological target for PD. In this study, we report that Fyn-mediated PKCδ tyrosine (Y311) phosphorylation is a key event preceding its proteolytic activation in a 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) model of Parkinsonism. MPP+/MPTP induced Fyn kinase activation in N27 DAergic neuronal cells and the mouse substantia nigra. PKCδ-Y311 phosphorylation by activated Fyn initiates the apoptotic caspase-signaling cascade during DAergic degeneration. Pharmacological attenuation of Fyn activity protected DAergic neurons from MPP+-induced degeneration in primary mesencephalic neuronal cultures. We further employed Fyn wild-type and Fyn knockout (KO) mice to confirm whether Fyn is a valid pharmacological target of DAergic neurodegeneration. Primary mesencephalic neurons from Fyn KO mice were greatly protected from MPP+-induced DAergic cell death, neurite loss and DA reuptake loss. Furthermore, Fyn KO mice were significantly protected from MPTP-induced PKCδ-Y311 phosphorylation, behavioral deficits and nigral DAergic degeneration. This study thus unveils a mechanism by which Fyn regulates PKCδ's pro-apoptotic function and DAergic degeneration. Pharmacological inhibitors directed at Fyn activation could prove to be a novel therapeutic target in the delay or halting of selective DAergic degeneration during PD.
Keywords: Fyn; PKCδ; kinase; neurodegeneration; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2021 Saminathan, Ghosh, Zhang, Song, Jin, Anantharam, Kanthasamy and Kanthasamy.
Conflict of interest statement
AGK and VA have an equity interest in PK Biosciences Corporation located in Ames, IA. AGK also has an equity interest in Probiome Therapeutics located in Ames, IA. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by Iowa State University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Environmental neurotoxic pesticide dieldrin activates a non receptor tyrosine kinase to promote PKCδ-mediated dopaminergic apoptosis in a dopaminergic neuronal cell model.Neurotoxicology. 2011 Oct;32(5):567-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.06.009. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Neurotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21801747 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Stress Disassembles Nuclear Architecture through Proteolytic Activation of PKCδ and Lamin B1 Phosphorylation in Neuronal Cells: Implications for Pathogenesis of Age-related Neurodegenerative Diseases.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 1:2024.11.01.621517. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.01.621517. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Apr 17;19:1549265. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1549265. PMID: 39554109 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Dopaminergic neurotoxicant 6-OHDA induces oxidative damage through proteolytic activation of PKCδ in cell culture and animal models of Parkinson's disease.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 1;256(3):314-23. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.07.021. Epub 2011 Aug 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21846476 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive astrocytes are key players in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurorepair in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease: focus on endogenous neurorestoration.Curr Aging Sci. 2013 Feb;6(1):45-55. doi: 10.2174/1874609811306010007. Curr Aging Sci. 2013. PMID: 23895521 Review.
-
Pivotal Role of Fyn Kinase in Parkinson's Disease and Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia: a Novel Therapeutic Target?Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Apr;58(4):1372-1391. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-02201-z. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33175322 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid hormone T3 induces Fyn modification and modulates palmitoyltransferase gene expression through αvβ3 integrin receptor in PC12 cells during hypoxia.Transl Neurosci. 2024 Aug 7;15(1):20220347. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0347. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39118829 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritizing Parkinson's disease risk genes in genome-wide association loci.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025 Apr 16;11(1):77. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00933-0. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2025. PMID: 40240380 Free PMC article.
-
The positive implication of natural antioxidants on oxidative stress-mediated diabetes mellitus complications.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;22(4):100424. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2024.100424. Epub 2024 Sep 10. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39674630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3,5,3'-Triiodo-L-Thyronine Regulates Actin Cytoskeleton Dynamic in The Differentiated PC-12 Cells during Hypoxia through An αvβ3 Integrin.Cell J. 2023 Apr 1;25(4):247-254. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.557501.1059. Cell J. 2023. PMID: 37210645 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn Signaling in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Potential and Therapeutic Implications.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Sep 15;2022:9112127. doi: 10.1155/2022/9112127. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 36157893 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afeseh Ngwa H., Kanthasamy A., Anantharam V., Song C., Witte T., Houk R., et al. (2009). Vanadium induces dopaminergic neurotoxicity via protein kinase cdelta dependent oxidative signaling mechanisms: relevance to etiopathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 240, 273–285. 10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anantharam V., Kitazawa M., Latchoumycandane C., Kanthasamy A., Kanthasamy A. G. (2004). Blockade of PKC proteolytic activation by loss of function mutants rescues mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (MMT)-induced apoptotic cell death. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1035, 271–289. 10.1196/annals.1332.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anantharam V., Kitazawa M., Wagner J., Kaul S., Kanthasamy A. G. (2002). Caspase-3-dependent proteolytic cleavage of protein kinase Cδ is essential for oxidative stress-mediated dopaminergic cell death after exposure to methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl. J. Neurosci. 22, 1738–1751. 10.1523/jneurosci.22-05-01738.2002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

