The Comparison of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid R(-)- and S(+)-Flurbiprofen Concentration After Intravenous Injection of Flurbiprofen Axetil in Human Subjects
- PMID: 33995057
- PMCID: PMC8120306
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.646196
The Comparison of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid R(-)- and S(+)-Flurbiprofen Concentration After Intravenous Injection of Flurbiprofen Axetil in Human Subjects
Abstract
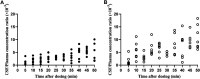
Background: Flurbiprofen axetil is a prodrug that releases the active substance through enzymatic removal of the ester moiety. It is formulated through encapsulation in a lipid microsphere carrier, and widely used to treat perioperative pain. Here, we studied the distribution of R (-)- and S (+)-flurbiprofen in human plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) after intravenous injection of flurbiprofen axetil. Methods: A total of 70 adult patients undergoing elective lower limb surgery under spinal anesthesia were given a single intravenous injection of 100-mg flurbiprofen axetil. The patients were randomly assigned to 10 groups for plasma and CSF sampling at 10 time points (5-50 min) after subarachnoid puncture and before actual spinal anesthesia. R (-)- and S (+)-flurbiprofen and CSF/plasma ratio were determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Results: R (-)-flurbiprofen concentration ranged from 2.01 to 10.9 μg/mL in plasma and 1.46-34.4 ng/mL in CSF. S (+)-flurbiprofen concentration ranged from 1.18 to 10.8 μg/mL in plasma and from 2.53 to 47 ng/mL in CSF. In comparison to S (+)-flurbiprofen, R (-)-flurbiprofen concentration was significantly higher in plasma at all time points (p < 0.05) except at 30 or 40 min, and lower in CSF at all time points (p < 0.05) except at 10, 15 and 40 min. Analysis after correcting drug concentration for body mass index also revealed higher plasma and lower CSF R (-)-flurbiprofen concentration. In comparison to S (+)-flurbiprofen, AUC0-50 for R (-)-flurbiprofen was larger in plasma and smaller in CSF (p < 0.05 for both), and accordingly smaller CSF/plasma AUC0-50 ratio (p < 0.05). There was a positive correlation between R (-)-flurbiprofen concentration and S (+)-flurbiprofen concentration in plasma (r = 0.725, p < 0.001) as well as in CSF (r = 0.718, p < 0.001), and a negative correlation between plasma and CSF concentration of S (+)-flurbiprofen (r = -0.250, p = 0.037), but not R (-)-flurbiprofen. Conclusion: Distribution of R (-)- and S (+)-flurbiprofen in plasma and CSF differed significantly. Penetration of R (-)-flurbiprofen into the CNS was lower than S (+)-flurbiprofen.
Keywords: R(-)-flurbiprofen; S(+)-flurbiprofen; cerebrospinal fluid; flurbiprofen axetil; plasma.
Copyright © 2021 Yao, Luo, Zhang, An, Feng and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Buvanendran A., Kroin J. S., Berger R. A., Hallab N. J., Saha C., Negrescu C., et al. (2006). Upregulation of Prostaglandin E2and Interleukins in the Central Nervous System and Peripheral Tissue during and after Surgery in Humans. Anesthesiol. 104 (3), 403–410. 10.1097/00000542-200603000-00005 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

