Boosting Akt Pathway by Rupatadine Modulates Th17/Tregs Balance for Attenuation of Isoproterenol-Induced Heart Failure in Rats
- PMID: 33995066
- PMCID: PMC8121023
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.651150
Boosting Akt Pathway by Rupatadine Modulates Th17/Tregs Balance for Attenuation of Isoproterenol-Induced Heart Failure in Rats
Abstract
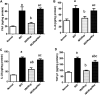
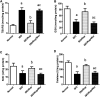
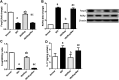
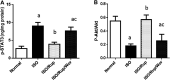
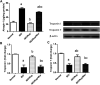
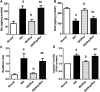
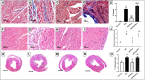
Disruption of Th17/Tregs homeostasis plays a crucial role in governing the immune response during myocardial fibrosis and its progression to heart failure. The present study aimed to assess for the first time the possible protection afforded by rupatadine against isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rats. It also explored the role of PI3k/Akt as a possible mechanistic pathway, through which rupatadine could modulate Th17/Tregs balance to display its effect. Isoproterenol (85 and 170 mg/kg/day) was injected subcutaneously for 2 successive days, respectively and rupatadine (4 mg/kg/day) was then given orally for 14 days with or without wortmannin (PI3K/Akt inhibitor). Rupatadine succeeded to completely ameliorate isoproterenol-induced cardiac dysfunction as demonstrated by improvements of electrocardiographic and echocardiographic measurements. Moreover, rupatadine prevented the marked elevation of PAF and oxidative stress in addition to Th17 promoting cytokines (IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β). Accordingly, rupatadine prevented Th17 stimulation or expansion as indicated by increased Foxp3/RORγt ratio and decreased production of its pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-17). Rupatadine treatment mitigated isoproterenol-induced activation of STAT-3 signaling and the imbalance in p-Akt/total Akt ratio affording marked decrease in atrogin-1 and apoptotic biomarkers. Finally, this therapy was effective in averting cardiac troponin loss and reverting the histological alterations as assessed by myocardial fibrosis and hypertrophy grading. Contrariwise, co-administration of wortmannin mostly attenuated the protective effects of rupatadine affording more or less similar results to that of isoproterenol-untreated rats. In conclusion, rupatadine could be an effective therapy against the development of isoproterenol-induced heart failure where PI3K/Akt pathway seems to play a crucial role in its protective effect.
Keywords: Akt; T helper 17; myocardial fibrosis; platelet activating factor; rupatadine.
Copyright © 2021 Ahmed, Mohamed, Abd El-Haleim and El-Tanbouly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardioprotective effect of nesfatin-1 against isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: Role of the Akt/GSK-3β pathway.Peptides. 2017 Sep;95:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Peptides. 2017. PMID: 28720397
-
The protective effect of kaempferol on heart via the regulation of Nrf2, NF-κβ, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathways in isoproterenol-induced heart failure in diabetic rats.Drug Dev Res. 2019 May;80(3):294-309. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21495. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Drug Dev Res. 2019. PMID: 30864233
-
Rupatadine, a new potent, orally active dual antagonist of histamine and platelet-activating factor (PAF).J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jan;280(1):114-21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 8996188
-
Fusaric acid (FA) protects heart failure induced by isoproterenol (ISP) in mice through fibrosis prevention via TGF-β1/SMADs and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Sep;93:130-145. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28624424
-
Regulatory B and T cell responses in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease and healthy controls.Dan Med J. 2016 Feb;63(2):B5177. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 26836805 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of injection of different doses of isoproterenol on the hearts of mice.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Sep 12;22(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02852-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 36096747 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Platelet-activating factor and HO-1 in mediating the protective effect of rupatadine against 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jun;29(26):40190-40203. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-18899-4. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35119631 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of crucial genes related to heart failure based on GEO database.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jul 28;23(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03400-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37507655 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis and biological evaluation reveals that LMO3 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.J Mol Histol. 2022 Apr;53(2):379-394. doi: 10.1007/s10735-021-10047-5. Epub 2022 Feb 14. J Mol Histol. 2022. PMID: 35165791
-
Lycorine ameliorates isoproterenol-induced cardiac dysfunction mainly via inhibiting inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress and apoptosis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5583-5594. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1967019. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34515620 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

