P2X7 Receptor-Mediated Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 33995071
- PMCID: PMC8117356
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.654425
P2X7 Receptor-Mediated Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
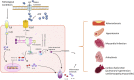
Purinergic P2X7 receptor, a nonselective cation channel, is highly expressed in immune cells as well as cardiac smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Its activation exhibits to mediate nucleotide-binding domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation, resulting in the release of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), and pyroptosis, thus triggering inflammatory response. These pathological mechanisms lead to the deterioration of various cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, pulmonary vascular remodeling, and cardiac fibrosis. All these worsening cardiac phenotypes are proven to be attenuated after the P2X7 receptor inhibition in experimental studies. The present review aimed to summarize key aspects of P2X7 receptor-mediated inflammation and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. The main focus is on the evidence addressing the involvement of the P2X7 receptor in the inflammatory responses to the occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease and therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: P2X7 receptor; arterial hypertension; atherosclerosis; inflammation; myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Zhou, Liu, Yin, Tang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

