Metabolic Changes Induced by Purinergic Signaling: Role in Food Intake
- PMID: 33995077
- PMCID: PMC8117016
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.655989
Metabolic Changes Induced by Purinergic Signaling: Role in Food Intake
Abstract
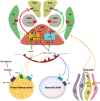
The purinergic signalling has a well-established role in the regulation of energy homeostasis, but there is growing evidence of its implication in the control of food intake. In this review, we provide an integrative view of the molecular mechanisms leading to changes in feeding behaviour within hypothalamic neurons following purinergic receptor activation. We also highlight the importance of purinergic signalling in metabolic homeostasis and the possibility of targeting its receptors for therapeutic purposes.
Keywords: food intake; metabolic homeostasis; obesity; orexigen and anorexigen neurons; purinergic receptors.
Copyright © 2021 Caruso, Zuccarini, Di Iorio, Muhammad and Ronci.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

