Edible and Herbal Plants for the Prevention and Management of COVID-19
- PMID: 33995078
- PMCID: PMC8113769
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.656103
Edible and Herbal Plants for the Prevention and Management of COVID-19
Abstract
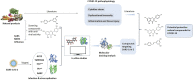
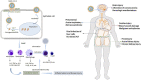
Background: The outbreak of the pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has now become a global pandemic spreading throughout the world. Unfortunately, due to the high infectiousness of the novel β-coronavirus, it is very likely to become an ordinary epidemic. The development of dietary supplements and functional foods might provide a strategy for the prevention and management of COVID-19. Scope and Approach: A great diversity of potential edible and medicinal plants and/or natural compounds showed potential benefits in managing SARS, which may also combat COVID-19. Moreover, many plants and compounds have currently been proposed to be protective against COVID-19. This information is based on data-driven approaches and computational chemical biology techniques. In this study, we review promising candidates of edible and medicinal plants for the prevention and management of COVID-19. We primarily focus on analyzing their underlying mechanisms. We aim to identify dietary supplements and functional foods that assist in managing this epidemic. Key findings and Conclusion: We infer that acetoside, glyasperin, isorhamnetin, and several flavonoid compounds may prevent and/or be effective in managing COVID-19 by targeting the viral infection, reducing the host cytokine storm, regulating the immune response, and providing organ protection. These bioactive dietary components (used either alone or in combination) might assist in the development of dietary supplements or functional foods for managing COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; cytokine storm; dietary supplements; functional foods; immune response; organ protection; virus infection.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Cheng, Zhang, Tang, Tan, Chen, Wang, Lai and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad A., Alkharfy K. M., Jan B. L., Ahad A., Ansari M. A., Al-Jenoobi F. I., et al. (2020a). Apr - May). Thymoquinone Treatment Modulates the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway and Abrogates the Inflammatory Response in an Animal Model of Lung Fibrosis. Exp. Lung Res. 46 (3-4), 53–63. 10.1080/01902148.2020.1726529 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

