A Quantitative Serum Proteomic Analysis Helps to Explore the Comprehensive Mechanism and Identify Serum Biomarkers of Shengmai Injection's Effect on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Rats
- PMID: 33995093
- PMCID: PMC8113823
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.666429
A Quantitative Serum Proteomic Analysis Helps to Explore the Comprehensive Mechanism and Identify Serum Biomarkers of Shengmai Injection's Effect on Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Ischemia in Rats
Abstract
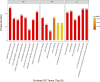
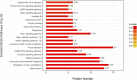
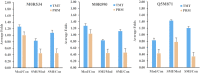
Shengmai injection (SMI), a traditional Chinese medicine formula with the nature of multicomponent and multi-target, has been widely used in clinic for treating cardiovascular diseases in China; however, its comprehensive mechanism of action remains unclear. In this study, a TMT-based quantitative serum proteomics was performed to explore SMI's global mechanism and help identify serum biomarkers of its effect on isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial ischemia rats. The results of TMT-based proteomic analysis identified 227, 100, and 228 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) for the model compared to the control group, SMI pretreatment + model compared to the model group, and SMI pretreatment + model compared to the control group, respectively. Based on bioinformatics analyses of gene ontology (GO), KEGG pathways, and the protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks for the DEPs, it is concluded that the comprehensive mechanism of SMI's effect on ISO-induced myocardial ischemia injury includes regulation of energy metabolism, reducing endothelial cell permeability, regulation of vessel and cardiac contractility, anti-inflammation, and prevention of cell apoptosis. Furthermore, 10 common DEPs were found, and six of them were regulated in model vs. control group, while back-regulated in SMI pretreatment + model vs. model group. Among them, three functional proteins of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 3 (FAIM3), and uncharacterized protein (M0R5J4), which were verified by the PRM analysis, might be the potential serum biomarkers on SMI's effects. Overall, this serum proteomics of SMI not only provides insights into the comprehensive mechanism underlying SMI's effects on ischemic heart disease but also helps identify serum biomarkers for directing SMI's cardioprotective effects.
Keywords: Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule 3; Shengmai injection; TMT; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; myocardial ischemia; serum biomarkers; serum proteomics.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zhang, Ji, Wei, Ding, Liu, Lv, Zheng and Zhan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abdelrady A. M., Zaitone S. A., Farag N. E., Fawzy M. S., Moustafa Y. M. (2017). Cardiotoxic effect of levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in rats with/without acute myocardial infarction: impact on cardiac rhythm and cardiac expression of Kv4.3, Kv1.2 and Nav1.5 channels. Biomed. Pharmacother. 92, 196 206. 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.049 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen C. Y., Lu L. Y., Chen P., Ji K. T., Lin J. F., Yang P. L., et al. (2013). Shengmai injection, a traditional Chinese patent medicine, for intradialytic hypotension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 703815. 10.1155/2013/703815 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

