Single Capsule Bismuth Quadruple Therapy for Eradication of H. pylori Infection: A Real-Life Study
- PMID: 33995097
- PMCID: PMC8118713
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.667584
Single Capsule Bismuth Quadruple Therapy for Eradication of H. pylori Infection: A Real-Life Study
Abstract
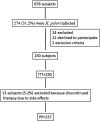
Background and aim: Bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT) or non-bismuth quadruple therapy (i.e., concomitant therapy) (CT) is the first-line regimens to eradicate H. pylori infection in areas with high prevalence of clarithromycin (CLA) resistance. Guidelines suggest that in areas of high prevalence of H. pylori strains with double resistance (i.e., CLA + metronidazole), BQT should be preferred to CT. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BQT administered through the three-in-one pill (Pylera) formulation in a large series of H. pylori-infected patients, naive to treatment in a region with high CLA and dual resistance. Patients and methods: We treated 250 patients (148 F and 102 M, mean age 48.6 years) with H. pylori infection naïve to treatment. Patients received esomeprazole 40 mg bid and Pylera 3 tablets qid for 10 days. Diagnosis of H. pylori infection was through 13C urea breath test (13C UBT), or stool antigen test or histology, as appropriate. The evaluation of eradication was through 13C UBT at least 45 days after the end of therapy. Incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was assessed through a questionnaire at the end of treatment. Compliance was considered good if at least 90% of medication had been taken. Statistical analysis was per intention-to-treat e per protocol (PP). 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Results: 1) 13 patients (5.2%) discontinued therapy due to side effects; 2) eradication rates in ITT and PP were 227/250 (90.8%; 95% CI 86.3-93.7%) and 226/237 (95.3%; 95% CI 91-99%), respectively; 3) the prevalence of TRAEs was 26.8%; and 4) adherence to treatment was good with compliance greater than 90%. Conclusion: In this real-life study, we demonstrate that in an area with a high prevalence of H. pylori strains with CLA or CLA + metronidazole resistance, BQT using Pylera is an effective therapeutic strategy with ITT eradication rates higher than 90%; this therapy is associated with good compliance and low incidence of side effects.
Keywords: BQT; H. pylori; bismuth quadruple therapy; eradication therapy; real life.
Copyright © 2021 Gravina, Priadko, Granata, Facchiano, Scidà, Cerbone, Ciamarra and Romano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy versus concomitant quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter Pylori infection in an area of high resistance to clarithromycin: A prospective, cross-sectional, comparative, open trial.Helicobacter. 2019 Feb;24(1):e12546. doi: 10.1111/hel.12546. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Helicobacter. 2019. PMID: 30346636 Clinical Trial.
-
The "three-in-one" formulation of bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication with or without probiotics supplementation: Efficacy and safety in daily clinical practice.Helicobacter. 2018 Aug;23(4):e12502. doi: 10.1111/hel.12502. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Helicobacter. 2018. PMID: 29924430 Clinical Trial.
-
Non-bismuth and bismuth quadruple therapies based on previous clarithromycin exposure are as effective and safe in an area of high clarithromycin resistance: A real-life study.Helicobacter. 2020 Aug;25(4):e12694. doi: 10.1111/hel.12694. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Helicobacter. 2020. PMID: 32314519
-
Meta-analysis of bismuth quadruple therapy versus clarithromycin triple therapy for empiric primary treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection.Digestion. 2013;88(1):33-45. doi: 10.1159/000350719. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Digestion. 2013. PMID: 23880479 Review.
-
Susceptibility-Guided Therapy vs. Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy as the First-Line Treatment for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 24;9:844915. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.844915. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35402425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multicentric Study to Assess Helicobacter pylori Incidence, Patient Reported Adverse Events, Compliance and Effectiveness, in Real-World Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 7;19(19):12847. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912847. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36232149 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Probiotics in the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and Overall Impact on Management of Peptic Ulcer: A Study Involving Patients Undergoing Triple Therapy in Bangladesh.Cureus. 2024 Mar 16;16(3):e56283. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56283. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38495972 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the potential of regulated cell death in glioma treatment: a focus on autophagy-dependent cell death, anoikis, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, pyroptosis, immunogenic cell death, and the crosstalk between them.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 9;14:1397863. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1397863. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39184045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Bismuth Quadruple Therapy Containing Tetracyclines Combined with Other Antibiotics and Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 28;11(23):7040. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237040. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Francesco V., Margiotta M., Zullo A., Hassan C., Valle N. D., Burattini O., et al. (2006). Claritromycin resistance and Helicobacter pylori genotypes in Italy. J. Microbiol. 44 (6), 660–664. - PubMed
-
- Di Ciaula A., Scaccianoce G., Venerito M., Zullo A., Bonfrate L., Rokkas T., et al. (2017). Eradication rates in Italian subjects heterogeneously managed for Helicobacter pylori infection. Time to abandon empiric treatments in Southern Europe. Jgld 26 (2), 129–137. 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.262.itl - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous