Photothermal Therapy via NIR II Light Irradiation Enhances DNA Damage and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress for Efficient Chemotherapy
- PMID: 33995101
- PMCID: PMC8117088
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.670207
Photothermal Therapy via NIR II Light Irradiation Enhances DNA Damage and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress for Efficient Chemotherapy
Abstract
Ovarian cancer has the highest death rate in gynecologic tumors and the main therapy for patients with advanced is chemotherapy based on cisplatin. Additionally, hyperthermic intraperitoneal has been used in clinic to obtain better efficacy for patients. Hence, combined photothermal therapy with platinum drugs in a new delivery system might bring new hope for ovarian cancer. A reduction sensitive polymer encapsulating a Pt (IV) prodrug and a near infrared II (NIR II) photothermal agent IR1048 to form nanoparticles were reported to enhance the efficacy of ovarian cancer treatment. At the same time, endoplasmic reticulum stress indicates an imbalance in proteostasis which probably caused by extrinsic stress such as chemotherapy and the temperature changed. The efficacy of nanoparticles containing Pt (IV) and IR1048 under NIR II light might be caused via increased DNA damage and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress.
Keywords: DNA damage; NIR II light; chemotherapy; endoplasmic reticulum stress key; mild hyperthermia; photothermal therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Kong, Wei, Xie, Wang, Yu, Kang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor and the reviewer (PM) declared a shared affiliation with the authors at time of review.
Figures

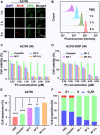
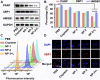
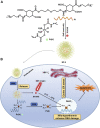
References
-
- Balakrishnan P. B., Silvestri N., Fernandez‐Cabada T., Marinaro F., Fernandes S., Fiorito S., et al. (2020). Exploiting Unique Alignment of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles, Mild Hyperthermia, and Controlled Intrinsic Cobalt Toxicity for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 32 (45), 2003712. 10.1002/adma.202003712 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

