Pioglitazone for NAFLD Patients With Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33995271
- PMCID: PMC8115121
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.615409
Pioglitazone for NAFLD Patients With Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Pioglitazone for NAFLD Patients With Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 16;13:840299. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.840299. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35250889 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To systematically evaluate the effects of pioglitazone in the treatment of patients with prediabetes or T2DM combined with NAFLD.
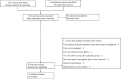
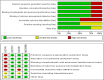
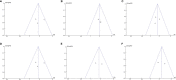
Methods: The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Embase, and ClinicalTrials databases were searched until August 2020 for publications written in English. Two reviewers independently assessed study eligibility, continuous data extraction, independent assessment of bias risk, and graded the strength of evidence. Our primary outcomes were the individual number of patients with improvement of at least 1 point in each of the histological parameters. Baseline characteristic data, such as BMI, weight, total body fat, fasting plasma glucose and fasting plasma insulin, and liver biological indicators, such as triglyceride level, HDL cholesterol level, plasma AST, and plasma ALT, were used as secondary outcomes.
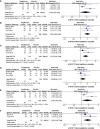
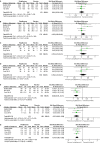
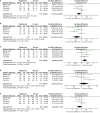
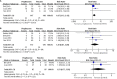
Results: A total of 4 studies were included. Compared with placebo, pioglitazone significantly improved steatosis grade, inflammation grade and ballooning grade, while in the fibrosis stage, there was no significant improvement in pioglitazone compared with placebo. In addition, pioglitazone can also improve blood glucose and liver function.
Conclusion: Pioglitazone can significantly improve the histological performance of the liver and insulin sensitivity. Additionally, it can significantly reduce fasting blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, plasma AST, ALT and other liver biological indicators. Due to the lack of relevant randomized controlled trials and short intervention times, long-term studies are still needed to verify its efficacy and safety.
Systematic review registration: [PROSPERO], identifier [CRD42020212025].
Keywords: NAFLD; meta-analysis; pioglitazone; prediabetes; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2021 Lian and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sberna AL, Bouillet B, Rouland A, Brindisi MC, Nguyen A, Mouillot T, et al. European Association for the Study of the Liver (Easl), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) Clinical Practice Recommendations for the Management of non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Evaluation of Their Application in People With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Med (2018) 35(3):368–75. doi: 10.1111/dme.13565 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jang JE, Cho Y, Lee BW, Shin ES, Lee SH. Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab J (2019) 43(3):302–18. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0062 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

