FGF21 Serum Levels in the Early Second Trimester Are Positively Correlated With the Risk of Subsequent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity-Matched Nested Case-Control Study
- PMID: 33995273
- PMCID: PMC8113961
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.630287
FGF21 Serum Levels in the Early Second Trimester Are Positively Correlated With the Risk of Subsequent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity-Matched Nested Case-Control Study
Abstract
Background: As an important endocrine hormone regulating glucose metabolism, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is increased in individuals with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) after 24 gestational weeks. However, it is unknown whether the increase in FGF21 precedes the diagnosis of GDM.
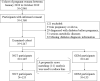
Methods: In this nested case-control study, 133 pregnant women with GDM and 133 pregnant women with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) were identified through propensity score matching, and serum FGF21 levels were measured at 14 to 21 gestational weeks, before GDM is routinely identified. The differences in FGF21 levels were compared. The association between FGF21 and the occurrence of GDM was evaluated using logistic regression models with adjustment for confounders.
Results: The serum FGF21 levels of the GDM group at 14 to 21 gestational weeks were significantly higher than those of the NGT group overall (P < 0.001), with similar results observed between the corresponding BMI subgroups (P < 0.05). The 2nd (OR 1.224, 95% CI 0.603-2.485), 3rd (OR 2.478, 1.229-5.000), and 4th (OR 3.419, 95% CI 1.626-7.188) FGF21 quartiles were associated with greater odds of GDM occurrence than the 1st quartile after multivariable adjustments.
Conclusions: The serum FGF21 levels in GDM groups increased in the early second trimester, regardless of whether participants were stratified according to BMI. After adjusting for confounding factors, the FGF21 levels in the highest quartile were associated with more than three times higher probability of the diagnosis of GDM in the pregnancy as compared to levels in the first quartile.
Keywords: FGF21; early second trimester; gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM); nested case-control study; propensity score matching (PSM).
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Yuan, Xu, Zhang, Ying and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jan 16;25(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07157-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 39819596 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Elevated Plasma FGF21 and Activated FGF21 Signaling in Visceral White Adipose Tissue and Improved Insulin Sensitivity in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Subtype: A Case-Control Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 29;12:795520. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.795520. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34912302 Free PMC article.
-
Serum concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: association with insulin resistance, adiponectin, and polycystic ovary syndrome history.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e81190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081190. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260557 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal overweight and obesity modify the association of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels with gestational diabetes mellitus: A nested case-control study.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024 Jan;40(1):e3717. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3717. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37649397
-
Hepatokine levels during the first or early second trimester of pregnancy and the subsequent risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomarkers. 2021 Sep;26(6):517-531. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.1928754. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Biomarkers. 2021. PMID: 34082623
Cited by
-
Progress in Research on Biomarkers of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Nov 22;16:3807-3815. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S433179. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 38028997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between serum adipokine fibroblast growth factor-21 and gestational diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Dec;13(12):2047-2053. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13889. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 35871469 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jan 16;25(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07157-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 39819596 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Elevated Plasma FGF21 and Activated FGF21 Signaling in Visceral White Adipose Tissue and Improved Insulin Sensitivity in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Subtype: A Case-Control Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 29;12:795520. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.795520. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34912302 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the FGF19 Family in the Pathogenesis of Gestational Diabetes: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 9;24(24):17298. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417298. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous