Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Ceftazidime Resistance Is Caused by the Pyruvate Cycle Perturbation and Reverted by Fe3 + in Edwardsiella tarda
- PMID: 33995314
- PMCID: PMC8113649
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.654783
Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Ceftazidime Resistance Is Caused by the Pyruvate Cycle Perturbation and Reverted by Fe3 + in Edwardsiella tarda
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Ceftazidime Resistance Is Caused by the Pyruvate Cycle Perturbation and Reverted by Fe3+ in Edwardsiella tarda.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 6;12:778578. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.778578. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34691013 Free PMC article.
Abstract
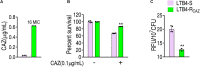
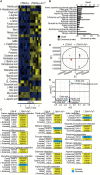
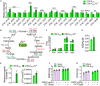
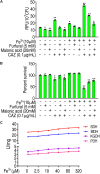
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are related to antibiotic resistance and have been reported in bacteria. However, whether ROS contribute to ceftazidime resistance and plays a role in ceftazidime-mediated killing is unknown. The present study showed lower ROS production in ceftazidime-resistant Edwardsiella tarda (LTB4-R CAZ ) than that in LTB4-sensitive E. tarda (LTB4-S), two isogenic E. tarda LTB4 strains, which was related to bacterial viability in the presence of ceftazidime. Consistently, ROS promoter Fe3+ and inhibitor thiourea elevated and reduced the ceftazidime-mediated killing, respectively. Further investigation indicated that the reduction of ROS is related to inactivation of the pyruvate cycle, which provides sources for ROS biosynthesis, but not superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), which degrade ROS. Interestingly, Fe3+ promoted the P cycle, increased ROS biosynthesis, and thereby promoted ceftazidime-mediated killing. The Fe3+-induced potentiation is generalizable to cephalosporins and clinically isolated multidrug-resistant pathogens. These results show that ROS play a role in bacterial resistance and sensitivity to ceftazidime. More importantly, the present study reveals a previously unknown mechanism that Fe3+ elevates ROS production via promoting the P cycle.
Keywords: Edwardsiella tarda; antibiotic resistance; ceftazidime; reactive oxygen species; the pyruvate cycle.
Copyright © 2021 Ye, Su, Peng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Corrigendum: Reactive Oxygen Species-Related Ceftazidime Resistance Is Caused by the Pyruvate Cycle Perturbation and Reverted by Fe3+ in Edwardsiella tarda.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 6;12:778578. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.778578. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34691013 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Is Associated with the Acquisition of Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Edwardsiella tarda.mSystems. 2021 Aug 31;6(4):e0069421. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00694-21. Epub 2021 Aug 24. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34427511 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrite Promotes ROS Production to Potentiate Cefoperazone-Sulbactam-Mediated Elimination to Lab-Evolved and Clinical-Evolved Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0232721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02327-21. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35863024 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam and underlying mechanisms.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020 Sep;22:18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2019.12.009. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020. PMID: 31863899 Review.
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous NADH promotes the bactericidal effect of aminoglycoside antibiotics against Edwardsiella tarda.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2367647. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2367647. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38884466 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics analysis of the lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14917 response to antibiotic stress.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jun 28;24(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03385-3. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38943061 Free PMC article.
-
Current Promising Strategies against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;12(1):67. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010067. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Investigation of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Cefiderocol against Escherichia coli.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0109322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01093-22. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35980225 Free PMC article.
-
The Thioredoxin System in Edwardsiella piscicida Contributes to Oxidative Stress Tolerance, Motility, and Virulence.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 24;11(4):827. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11040827. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37110252 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

