Transcriptional Profiling of Myceliophthora thermophila on Galactose and Metabolic Engineering for Improved Galactose Utilization
- PMID: 33995328
- PMCID: PMC8113861
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.664011
Transcriptional Profiling of Myceliophthora thermophila on Galactose and Metabolic Engineering for Improved Galactose Utilization
Abstract
Efficient biological conversion of all sugars from lignocellulosic biomass is necessary for the cost-effective production of biofuels and commodity chemicals. Galactose is one of the most abundant sugar in many hemicelluloses, and it will be important to capture this carbon for an efficient bioconversion process of plant biomass. Thermophilic fungus Myceliophthora thermophila has been used as a cell factory to produce biochemicals directly from renewable polysaccharides. In this study, we draw out the two native galactose utilization pathways, including the Leloir pathway and oxido-reductive pathway, and identify the significance and contribution of them, through transcriptional profiling analysis of M. thermophila and its mutants on galactose. We find that galactokinase was necessary for galactose transporter expression, and disruption of galK resulted in decreased galactose utilization. Through metabolic engineering, both galactokinase deletion and galactose transporter overexpression can activate internal the oxido-reductive pathway and improve the consumption rate of galactose. Finally, the heterologous galactose-degradation pathway, De Ley-Doudoroff (DLD) pathway, was successfully integrated into M. thermophila, and the consumption rate of galactose in the engineered strain was increased by 57%. Our study focuses on metabolic engineering for accelerating galactose utilization in a thermophilic fungus that will be beneficial for the rational design of fungal strains to produce biofuels and biochemicals from a variety of feedstocks with abundant galactose.
Keywords: Myceliophthora; galactose transport; galactose utilization; metabolic engineering; transcriptomic profiles.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Sun, Zhao, Gu, Liu, Wu, Wang, Tian and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer LL declared a shared affiliation, with the authors HW and DW to the handling editor at the time of the review.
Figures
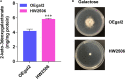
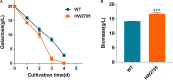
References
-
- Azar S. R., Naiebi R., Homami A., Akbari Z., Kianmehr A., Mahdizadehdehosta R., et al. (2015). Expression and response surface optimization of the recovery and purification of recombinant D-galactose dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 52 68–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

