Gene Expression Patterns for Proteins With Lectin Domains in Flax Stem Tissues Are Related to Deposition of Distinct Cell Wall Types
- PMID: 33995436
- PMCID: PMC8121149
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2021.634594
Gene Expression Patterns for Proteins With Lectin Domains in Flax Stem Tissues Are Related to Deposition of Distinct Cell Wall Types
Abstract
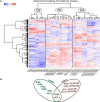
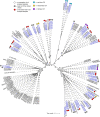
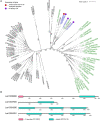
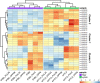
The genomes of higher plants encode a variety of proteins with lectin domains that are able to specifically recognize certain carbohydrates. Plants are enriched in a variety of potentially complementary glycans, many of which are located in the cell wall. We performed a genome-wide search for flax proteins with lectin domains and compared the expression of the encoding genes in different stem tissues that have distinct cell wall types with different sets of major polysaccharides. Over 400 genes encoding proteins with lectin domains that belong to different families were revealed in the flax genome; three quarters of these genes were expressed in stem tissues. Hierarchical clustering of the data for all expressed lectins grouped the analyzed samples according to their characteristic cell wall type. Most lectins differentially expressed in tissues with primary, secondary, and tertiary cell walls were predicted to localize at the plasma membrane or cell wall. These lectins were from different families and had various architectural types. Three out of four flax genes for proteins with jacalin-like domains were highly upregulated in bast fibers at the stage of tertiary cell wall deposition. The dynamic changes in transcript level of many genes for lectins from various families were detected in stem tissue over the course of gravitropic response induced by plant gravistimulation. The data obtained in this study indicate a large number of lectin-mediated events in plants and provide insight into the proteins that take part in tissue specialization and reaction to abiotic stress.
Keywords: amaranthin; cell wall; flax; gene expression; gravitropic reaction; jacalin; malectin; plant lectins.
Copyright © 2021 Petrova, Nazipova, Gorshkov, Mokshina, Patova and Gorshkova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Using FIBexDB for In-Depth Analysis of Flax Lectin Gene Expression in Response to Fusarium oxysporum Infection.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;11(2):163. doi: 10.3390/plants11020163. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050051 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Wall Layer Induced in Xylem Fibers of Flax Upon Gravistimulation Is Similar to Constitutively Formed Cell Walls of Bast Fibers.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Apr 6;12:660375. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.660375. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33936149 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic lignification in the flax lignified bast fiber1 mutant stem is associated with tissue-specific modifications in gene expression and cell wall composition.Plant Cell. 2014 Nov;26(11):4462-82. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.130443. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25381351 Free PMC article.
-
Flax tubulin and CesA superfamilies represent attractive and challenging targets for a variety of genome- and base-editing applications.Funct Integr Genomics. 2020 Jan;20(1):163-176. doi: 10.1007/s10142-019-00667-2. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 30826923 Review.
-
Lectin domains at the frontiers of plant defense.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Aug 13;5:397. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00397. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25165467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using FIBexDB for In-Depth Analysis of Flax Lectin Gene Expression in Response to Fusarium oxysporum Infection.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;11(2):163. doi: 10.3390/plants11020163. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050051 Free PMC article.
-
Growing Maize Root: Lectins Involved in Consecutive Stages of Cell Development.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;11(14):1799. doi: 10.3390/plants11141799. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35890433 Free PMC article.
-
Phoenix dactylifera (date palm; Arecaceae) putative lectin homologs: Genome-wide search, architecture analysis, and evolutionary relationship.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):103676. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103676. Epub 2023 May 4. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37213699 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome map and genome annotation of flax line 3896.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 16;16:1520832. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1520832. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40453339 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Almeras T., Petrova A., Kozlova L., Gril J., Gorshkova T. (2020). Evidence and quantitative evaluation of tensile maturation strain in flax phloem through longitudinal splitting. Botany 98 9–19. 10.1139/cjb-2019-0021 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

